-
The enteral feeding tube access route in esophageal cancer surgery in Japan: a retrospective cohort study
-
Hiroyuki Kitagawa, Keiichiro Yokota, Tsutomu Namikawa, Kazuhiro Hanazaki
-
Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):58-65. Published online April 1, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0003
-
-
 Graphical Abstract Graphical Abstract
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
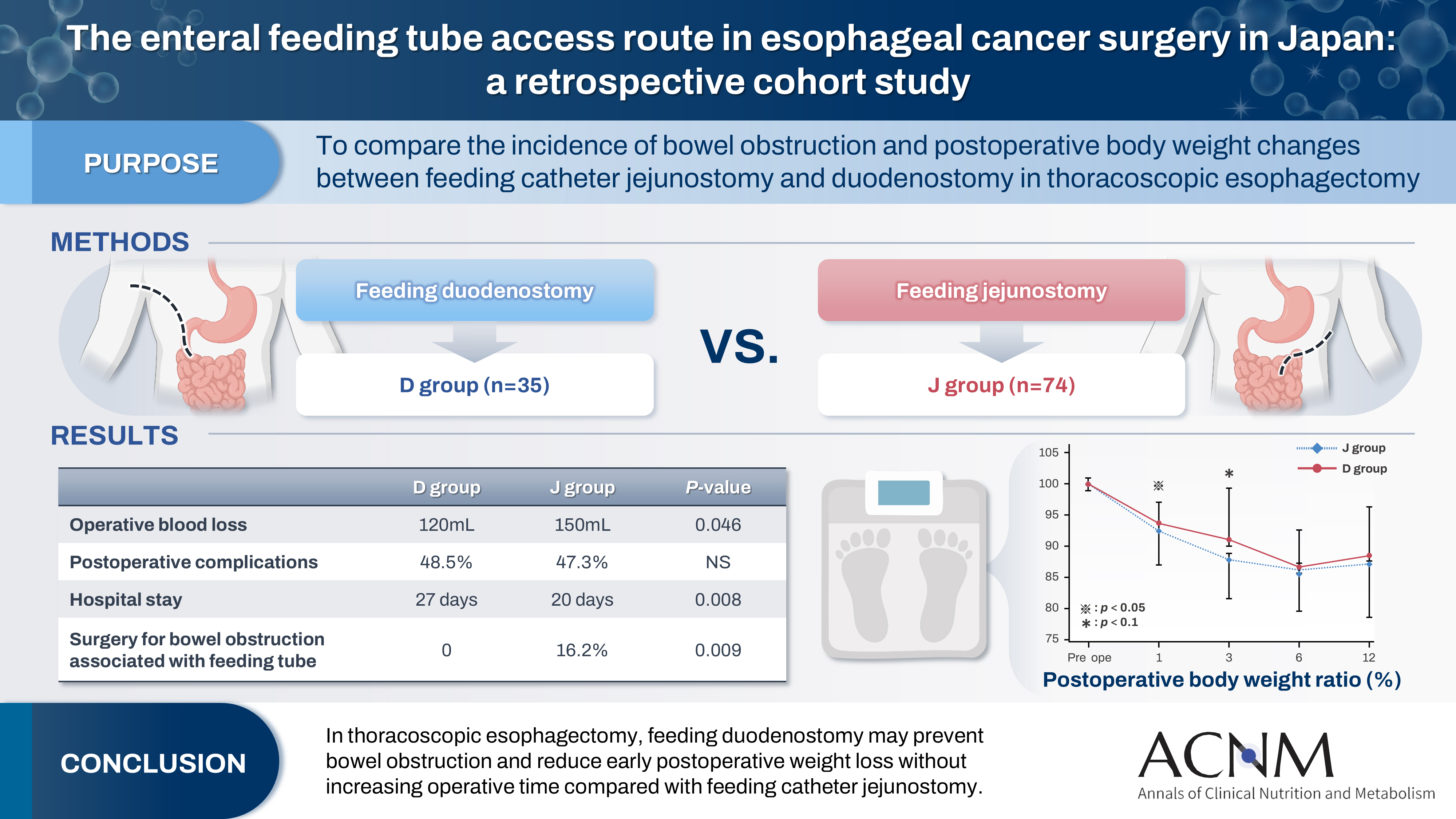 - Purpose
Feeding catheter jejunostomy is a useful access route for early enteral nutrition during esophageal cancer surgery. However, it may lead to postoperative bowel obstruction associated with feeding jejunostomy (BOFJ). To prevent BOFJ, we introduced feeding catheter duodenostomy via the round ligament in 2018. This study aimed to compare the incidence of BOFJ and postoperative body weight changes between feeding catheter jejunostomy and duodenostomy.
Methods
A total of 109 patients who underwent thoracoscopic esophagectomy and gastric tube reconstruction for esophageal cancer at Kochi Medical School Hospital between March 2013 and November 2020 were included. Preoperative patient characteristics (age, sex, preoperative weight, body mass index, cancer stage, and preoperative treatment), surgical outcomes (operative time, blood loss, and postoperative complications [wound infection, pneumonia, anastomotic leakage, BOFJ]), and body weight changes at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-surgery were compared between the jejunostomy (J) and duodenostomy (D) groups.
Results
The D group consisted of 35 patients. No significant differences were observed between the groups regarding age, sex, weight, body mass index, cancer stage, operative time, postoperative complications, or duration of tube placement. However, the D group had a significantly lower rate of preoperative chemotherapy (45.7% vs. 78.4%, P=0.001) and lower operative blood loss (120 mL vs. 150 mL, P=0.046) than the J group. All 12 cases of BOFJ occurred in the J group. Furthermore, the D group experienced a significantly lower weight loss ratio at 1 month postoperatively (93.9% vs. 91.8%, P=0.039).
Conclusion
In thoracoscopic esophagectomy, feeding duodenostomy may prevent bowel obstruction and reduce early postoperative weight loss without increasing operative time compared with feeding catheter jejunostomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
Ye Rim Chang
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 95. CrossRef
-
2,817
View
-
30
Download
-
1
Crossref
|







