Indexed in:
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Peripheral vein infusions of amino acids prevent early postoperative weight loss after robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy: a retrospective study in Japan
- Tomonori Narita, Kazuhiko Fukatsu, Satoshi Murakoshi, Reo Inoue, Kenichi Kono, Midori Noguchi, Nana Matsumoto, Shoh Yajima, Koichi Yagi, Yoshifumi Baba
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):149-155. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0012
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Purpose
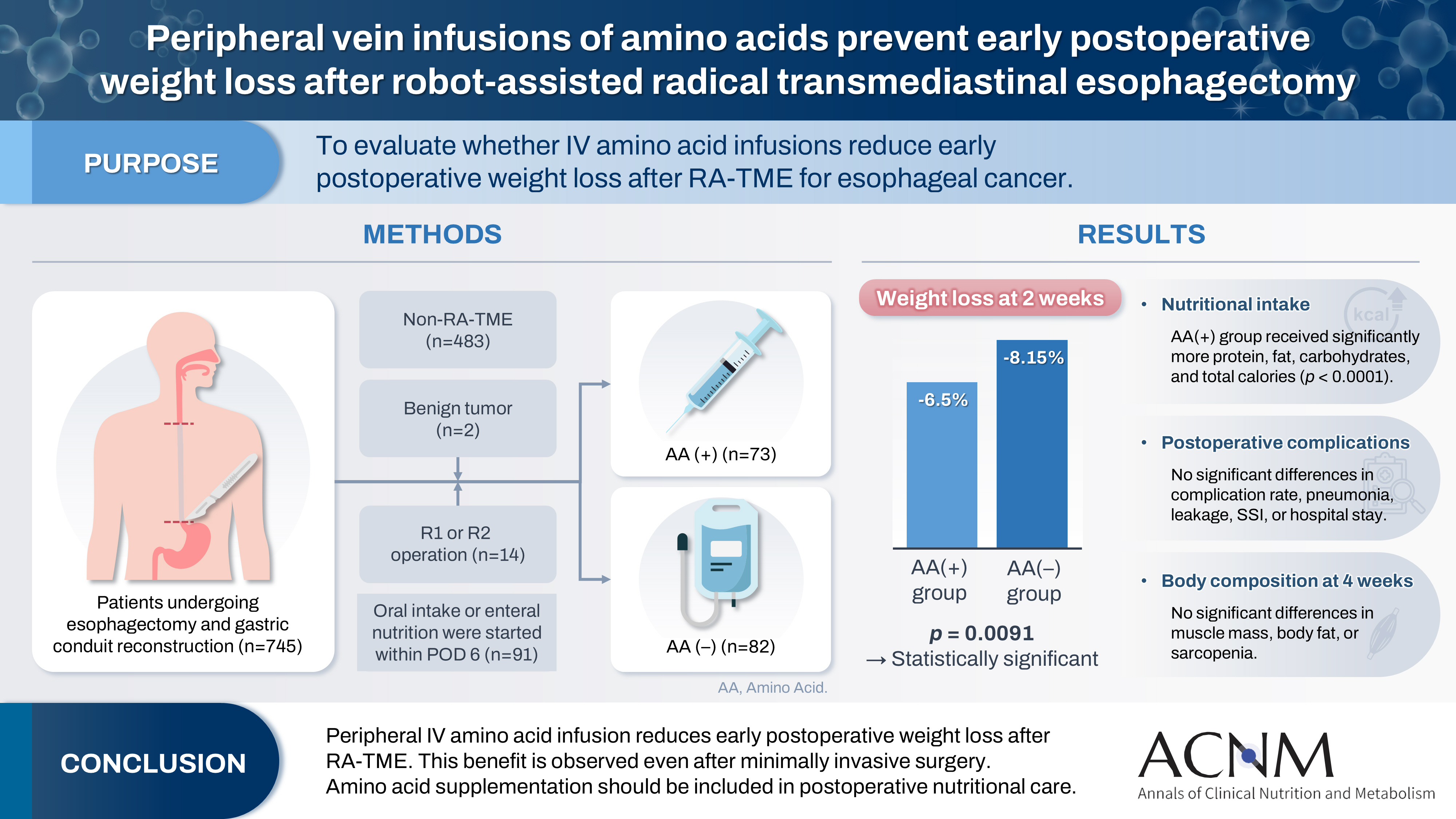
Postoperative body weight loss (PBWL) is linked to poor long-term outcomes following esophagectomy for esophageal cancer, making perioperative nutrition critically important. Although minimally invasive procedures such as robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy (RA-TME) have become more prevalent, less attention has been paid to perioperative nutritional management. This study evaluates the impact of intravenous (IV) amino acid infusions on PBWL in patients undergoing RA-TME.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 155 patients who underwent RA-TME for esophageal or esophagogastric junction cancer at our hospital between 2011 and 2022. Patients were divided into two groups: AA(+) (n=73, received IV amino acids between postoperative days 1–6) and AA(–) (n=82, did not receive IV amino acids). Oral or enteral nutrition was withheld until postoperative day 6. We compared nutrient intake, postoperative outcomes, and nutritional status between groups.
Results
Patient backgrounds, surgical outcomes, and complication rates were similar in both groups. However, the AA(+) group received significantly greater energy and nutrient intake. PBWL at 2 weeks post-surgery was significantly lower in the AA(+) group than in the AA(–) group (6.50% vs. 8.15%, P=0.0091).
Conclusion
IV amino acid infusion may help mitigate early PBWL after RA-TME.
- 1,184 View
- 17 Download

- The enteral feeding tube access route in esophageal cancer surgery in Japan: a retrospective cohort study
- Hiroyuki Kitagawa, Keiichiro Yokota, Tsutomu Namikawa, Kazuhiro Hanazaki
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):58-65. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0003
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
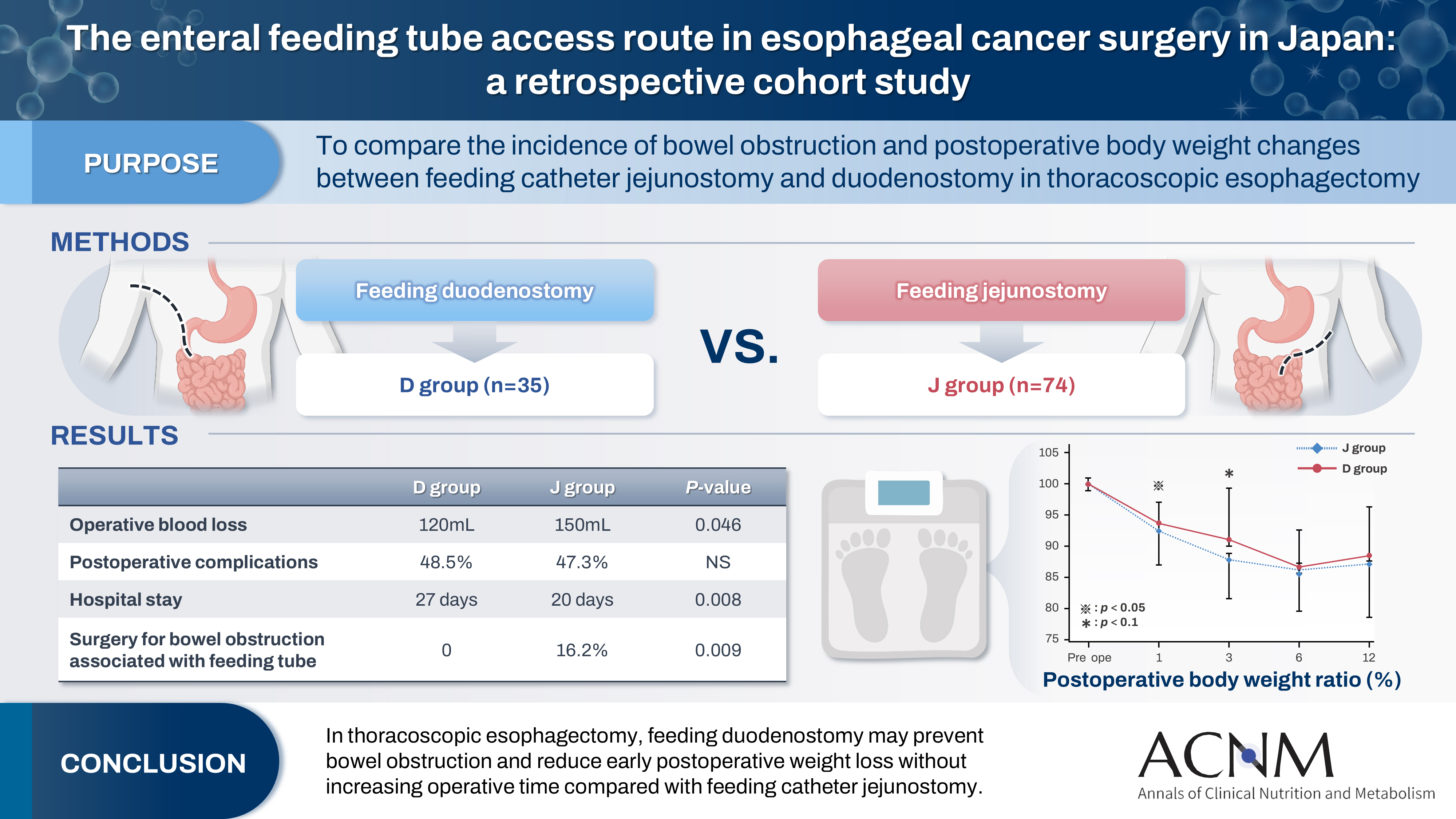
Feeding catheter jejunostomy is a useful access route for early enteral nutrition during esophageal cancer surgery. However, it may lead to postoperative bowel obstruction associated with feeding jejunostomy (BOFJ). To prevent BOFJ, we introduced feeding catheter duodenostomy via the round ligament in 2018. This study aimed to compare the incidence of BOFJ and postoperative body weight changes between feeding catheter jejunostomy and duodenostomy.
Methods
A total of 109 patients who underwent thoracoscopic esophagectomy and gastric tube reconstruction for esophageal cancer at Kochi Medical School Hospital between March 2013 and November 2020 were included. Preoperative patient characteristics (age, sex, preoperative weight, body mass index, cancer stage, and preoperative treatment), surgical outcomes (operative time, blood loss, and postoperative complications [wound infection, pneumonia, anastomotic leakage, BOFJ]), and body weight changes at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-surgery were compared between the jejunostomy (J) and duodenostomy (D) groups.
Results
The D group consisted of 35 patients. No significant differences were observed between the groups regarding age, sex, weight, body mass index, cancer stage, operative time, postoperative complications, or duration of tube placement. However, the D group had a significantly lower rate of preoperative chemotherapy (45.7% vs. 78.4%, P=0.001) and lower operative blood loss (120 mL vs. 150 mL, P=0.046) than the J group. All 12 cases of BOFJ occurred in the J group. Furthermore, the D group experienced a significantly lower weight loss ratio at 1 month postoperatively (93.9% vs. 91.8%, P=0.039).
Conclusion
In thoracoscopic esophagectomy, feeding duodenostomy may prevent bowel obstruction and reduce early postoperative weight loss without increasing operative time compared with feeding catheter jejunostomy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
Ye Rim Chang
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 95. CrossRef
- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
- 2,484 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of efficacy of enteral versus parenteral nutrition in patients after esophagectomy in Malaysia: a prospective cohort study
- Ramizah Mohd Shariff, Sze Chee Tee, Shukri Jahit Mohammad, Khei Choong Khong
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):41-49. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.24.016
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
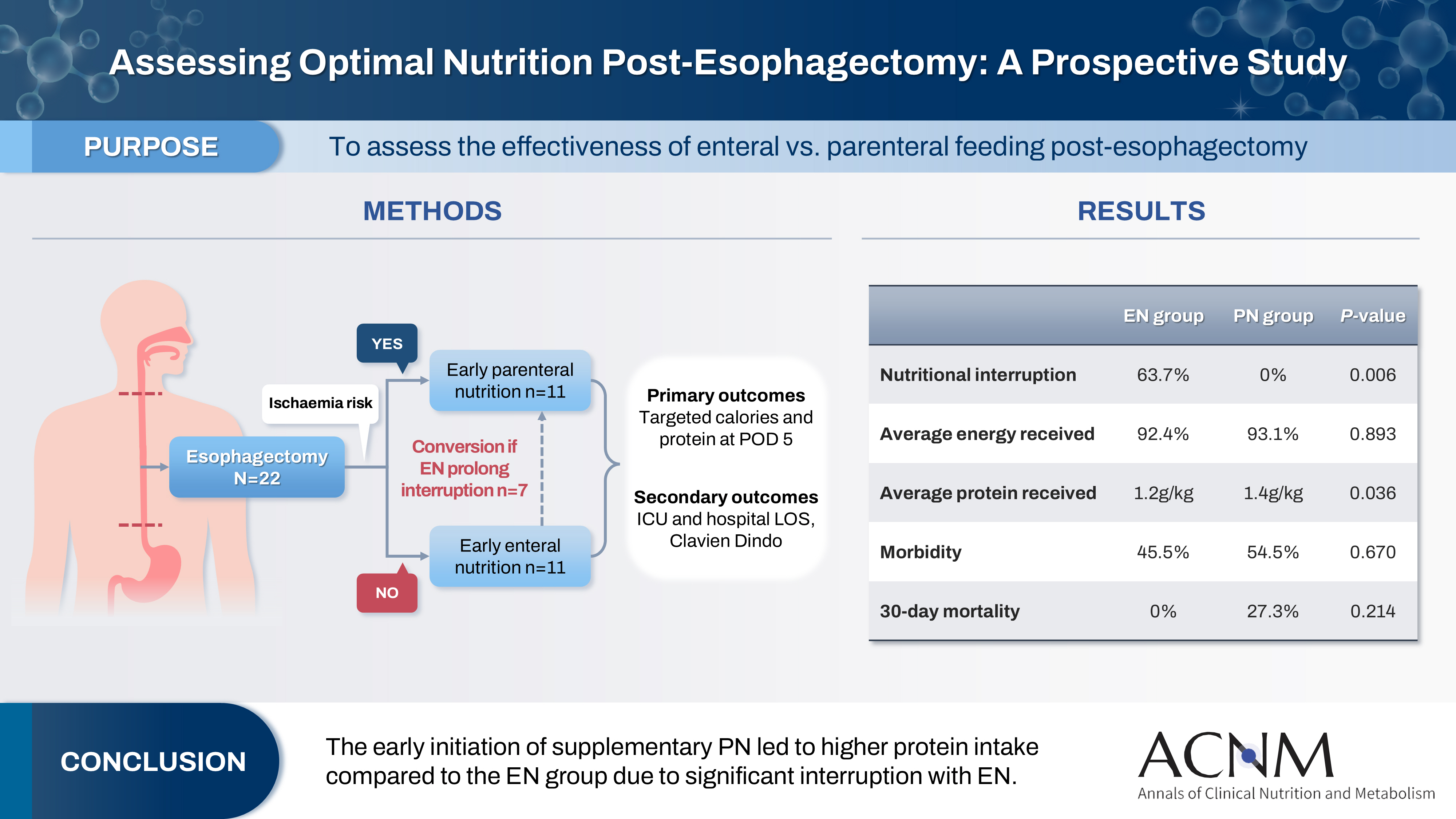
This study aims to assess the effectiveness of enteral versus parenteral feeding in patients after esophagectomy.
Methods
This a prospective cohort study of post-esophagectomy intensive care unit (ICU) patients over 12 months in the National Cancer Institute, Malaysia. Early enteral feeding followed the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery protocol, and parenteral nutrition (PN) was considered if there was a risk for conduit ischemia. It compared the effectiveness of enteral versus PN following esophagectomy, and assessed the correlations between biochemical nutritional markers and hospital lengths of stay or ventilation days.
Results
It included two cohorts receiving PN (n=11) or enteral nutrition (EN) (n=11) following elective esophagectomy. Preoperative weight, body mass index, and Subjective Global Assessment were higher in the EN group (P=0.033, P=0.021, P=0.031, respectively). Nutritional interruption occurred more frequently in the EN group (63.7%) compared to the PN group (P=0.001). Mean levels of energy and protein received were 93.1 kcal/kg and 1.4 g/kg for PN versus 92.4 kcal/kg and 1.2 g/kg for EN (P=0.893, P=0.036). The median lengths of ICU stay (P=0.688) and postoperative stay (P=0.947) between groups showed no significant difference. In addition, 30-day mortality (P=0.214) and other postoperative complications (P>0.05) were comparable in the two groups.
Conclusion
Early initiation of supplementary PN due to significant interruption in EN led to higher protein intake compared to the EN group. However, there were no significant differences in postoperative outcomes, including 30-day mortality, ICU length of stay, and ventilation days. PN ensures adequate nutritional intake, especially in terms of protein delivery, without adversely affecting postoperative recovery and clinical outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimizing nutritional support in upper gastrointestinal surgery: A comprehensive review of feeding jejunostomy techniques and outcomes
Ioana Alexandra Prisacariu, Konstantinos Eleftherios Koumarelas, Konstantinos Argyriou, Alexandros Charalabopoulos, Grigorios Christodoulidis
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Optimizing nutritional support in upper gastrointestinal surgery: A comprehensive review of feeding jejunostomy techniques and outcomes
- 5,177 View
- 63 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev


