Indexed in:
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Development of a Japanese version of the Short Bowel Syndrome-Quality of Life (SBS-QoL) scale
- Yuko Tazuke, Mayu Suzuki, Sae Kikuchi, Kaori Ishiguro, Hiroomi Okuyama
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):132-138. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0016
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
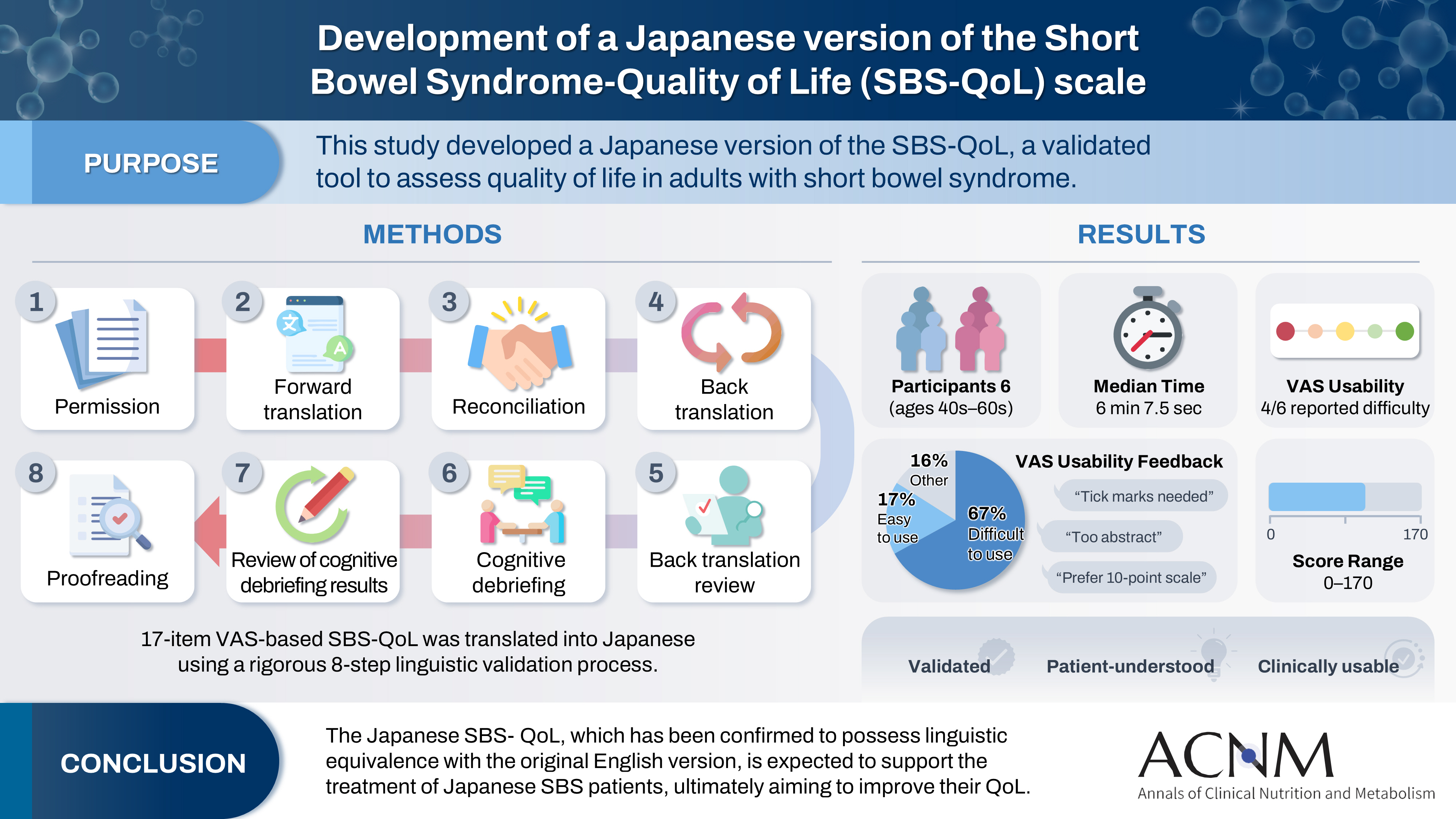
The Short Bowel Syndrome‐Quality of Life (SBS‐QoL) scale is a reliable and sensitive instrument developed to measure and evaluate the quality of life (QoL) in adult patients with short bowel syndrome (SBS). In Japan, increasing attention has been given to the assessment of QoL in patients with SBS; however, no Japanese‐language SBS‐specific scale is currently available. This study aimed to develop a Japanese version of the SBS‐QoL based on the original English version.
Methods
A provisional Japanese version was created in accordance with the guidelines of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) Task Force, utilizing a process of forward translation, adjustment, and back translation.
Results
Cognitive debriefing using the provisional Japanese version was conducted with six Japanese patients with SBS. Based on these results, the Japanese wording was evaluated and revised, leading to the creation of the final Japanese version.
Conclusion
The Japanese SBS‐QoL, which has been confirmed to possess linguistic equivalence with the original English version, is expected to support the treatment of Japanese SBS patients, ultimately aiming to improve their QoL.
- 1,643 View
- 19 Download

- Association between decreased dietary intake during hospitalization and long-term weight loss in postoperative gastric cancer patients over 75 years of age: a retrospective cohort study
- Daiki Tabe, Isao Miyajima, Akira Tsukada
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):75-84. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Weight loss following gastrectomy is a significant concern, and maintaining adequate nutrition is necessary, especially given the growing number of older adult patients. This study examined the relationship between postoperative food intake and long-term weight loss in postgastrectomy patients aged ≥75 years.
Methods
Out of 88 patients who underwent gastrectomy for gastric cancer at our institute, 46 were aged ≥75 years. These patients were divided into two groups: one with an average energy intake exceeding 50% of the basal metabolic rate and one with an intake below 50% of the basal metabolic rate. The percentage change in body weight up to 6 months post-surgery was compared between the groups.
Results
In the group with higher dietary intake, the rate of weight change at 3 and 6 months postoperatively was lower, and fewer patients received postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Poor postoperative food intake may serve as a predictor of weight loss up to 3 months following surgery in postgastrectomy patients aged ≥75 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
Ye Rim Chang
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 95. CrossRef
- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
- 1,079 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The enteral feeding tube access route in esophageal cancer surgery in Japan: a retrospective cohort study
- Hiroyuki Kitagawa, Keiichiro Yokota, Tsutomu Namikawa, Kazuhiro Hanazaki
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):58-65. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0003
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
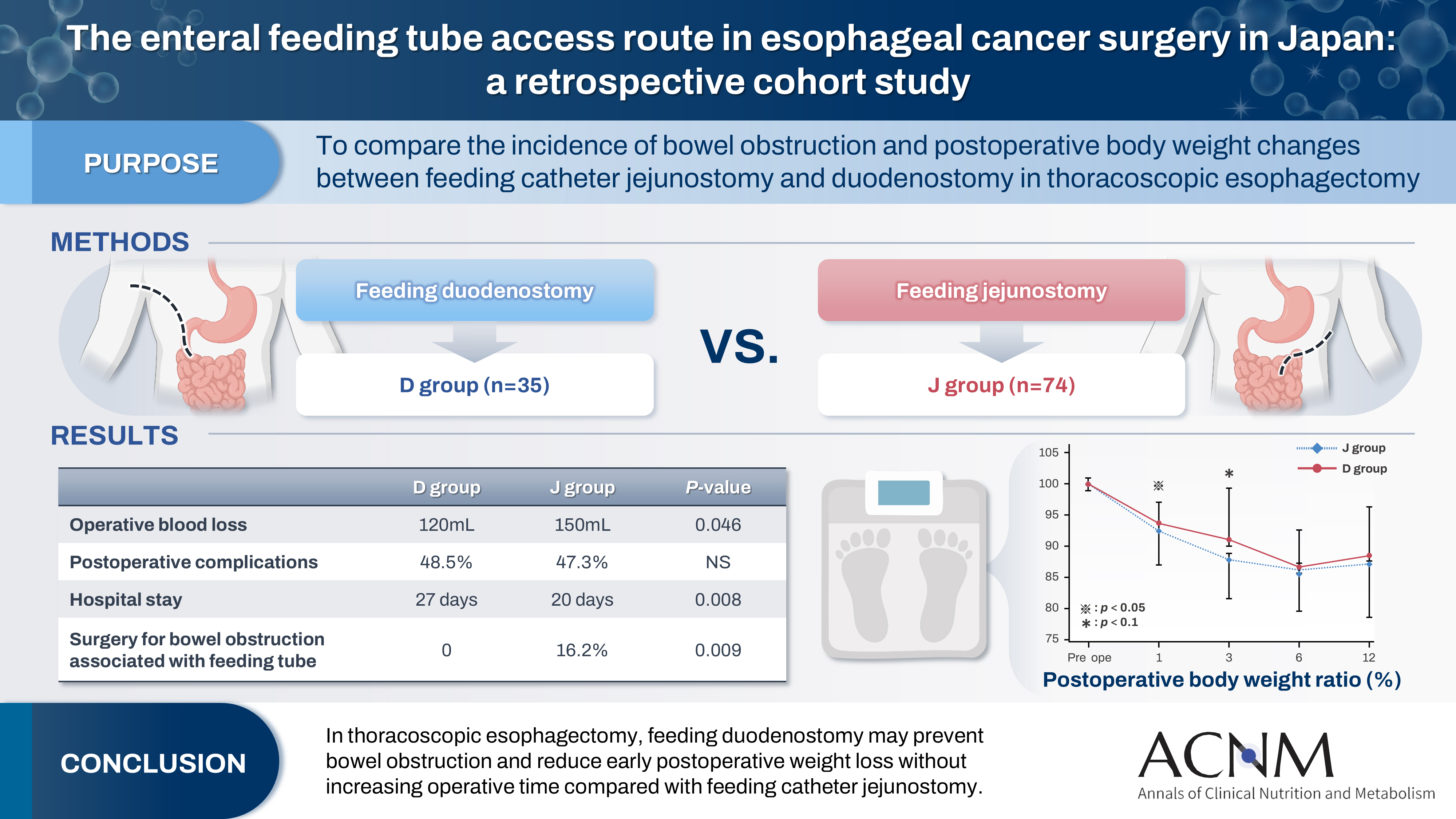
Feeding catheter jejunostomy is a useful access route for early enteral nutrition during esophageal cancer surgery. However, it may lead to postoperative bowel obstruction associated with feeding jejunostomy (BOFJ). To prevent BOFJ, we introduced feeding catheter duodenostomy via the round ligament in 2018. This study aimed to compare the incidence of BOFJ and postoperative body weight changes between feeding catheter jejunostomy and duodenostomy.
Methods
A total of 109 patients who underwent thoracoscopic esophagectomy and gastric tube reconstruction for esophageal cancer at Kochi Medical School Hospital between March 2013 and November 2020 were included. Preoperative patient characteristics (age, sex, preoperative weight, body mass index, cancer stage, and preoperative treatment), surgical outcomes (operative time, blood loss, and postoperative complications [wound infection, pneumonia, anastomotic leakage, BOFJ]), and body weight changes at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months post-surgery were compared between the jejunostomy (J) and duodenostomy (D) groups.
Results
The D group consisted of 35 patients. No significant differences were observed between the groups regarding age, sex, weight, body mass index, cancer stage, operative time, postoperative complications, or duration of tube placement. However, the D group had a significantly lower rate of preoperative chemotherapy (45.7% vs. 78.4%, P=0.001) and lower operative blood loss (120 mL vs. 150 mL, P=0.046) than the J group. All 12 cases of BOFJ occurred in the J group. Furthermore, the D group experienced a significantly lower weight loss ratio at 1 month postoperatively (93.9% vs. 91.8%, P=0.039).
Conclusion
In thoracoscopic esophagectomy, feeding duodenostomy may prevent bowel obstruction and reduce early postoperative weight loss without increasing operative time compared with feeding catheter jejunostomy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
Ye Rim Chang
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 95. CrossRef
- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
- 2,497 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Impact of postoperative nutritional status on the patients’ clinical outcomes and knee biomechanics following total knee arthroplasty in Japan: a prospective cohort study
- Kenichi Kono, Tetsuya Tomita, Takaharu Yamazaki, Masashi Tamaki, Shuji Taketomi, Ryota Yamagami, Reo Inoue, Yuki Taniguchi, Sakae Tanaka, Kazuhiko Fukatsu
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):50-57. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.24.019
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Purpose
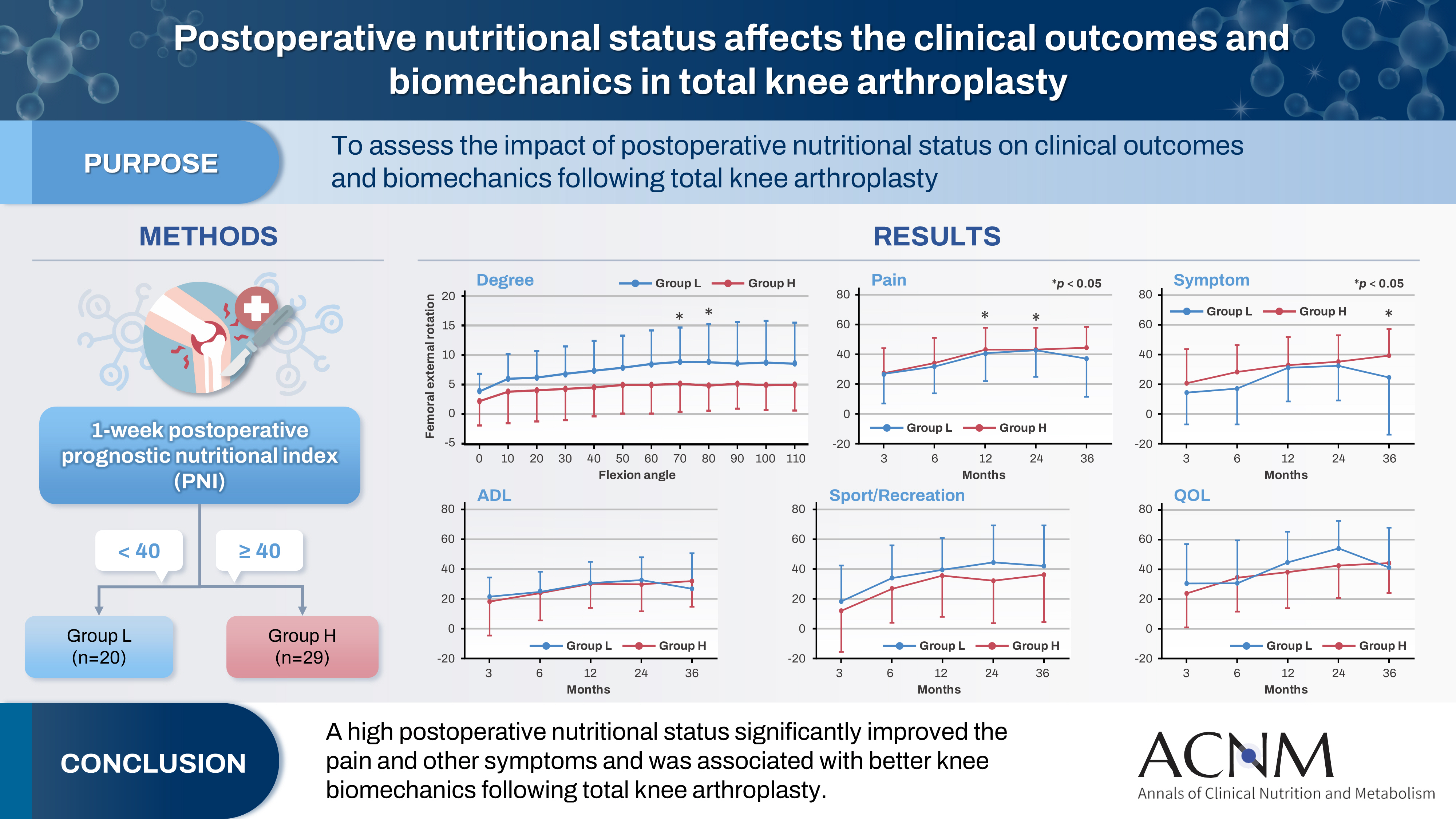
The impact of postoperative nutritional status on clinical outcomes and biomechanics following total knee arthroplasty remains largely unknown. This study aimed to assess this question using the prognostic nutritional index to evaluate the nutritional status of orthopedic participants.
Methods
Patients with knee osteoarthritis who underwent total knee arthroplasty (n=49) in Japan were divided into two groups based on their 1-week postoperative prognostic nutritional index. Group L patients had a prognostic nutritional index <40, whereas Group H comprised patients with a prognostic nutritional index ≥40. Postoperative improvements in Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score were evaluated. The patients performed squats under single-fluoroscopic surveillance in the sagittal plane for biomechanical evaluation. A two-dimensional/three-dimensional registration technique was employed to measure the tibiofemoral kinematics. The axial rotation of the femoral component relative to the tibial component and the anteroposterior translation of the medial and lateral femorotibial contact points were measured.
Results
Group H showed significantly higher pain scores than Group L at 12 and 36 months postoperatively and a significantly higher symptom score at 36 months postoperatively. The kinematic comparison revealed that the axial external rotation in Group L was larger than that in Group H from 70° to 80° with flexion. Moreover, in the medial anteroposterior translation, Group L was more anteriorly located than Group H, with flexion beyond 30°.
Conclusion
The results suggest that a high postoperative nutritional status significantly improved pain and other symptoms and was associated with better knee biomechanics following total knee arthroplasty.
- 2,504 View
- 37 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev


