Indexed in:
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed
Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Peripheral vein infusions of amino acids prevent early postoperative weight loss after robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy: a retrospective study in Japan
- Tomonori Narita, Kazuhiko Fukatsu, Satoshi Murakoshi, Reo Inoue, Kenichi Kono, Midori Noguchi, Nana Matsumoto, Shoh Yajima, Koichi Yagi, Yoshifumi Baba
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):149-155. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0012
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material 
- Purpose
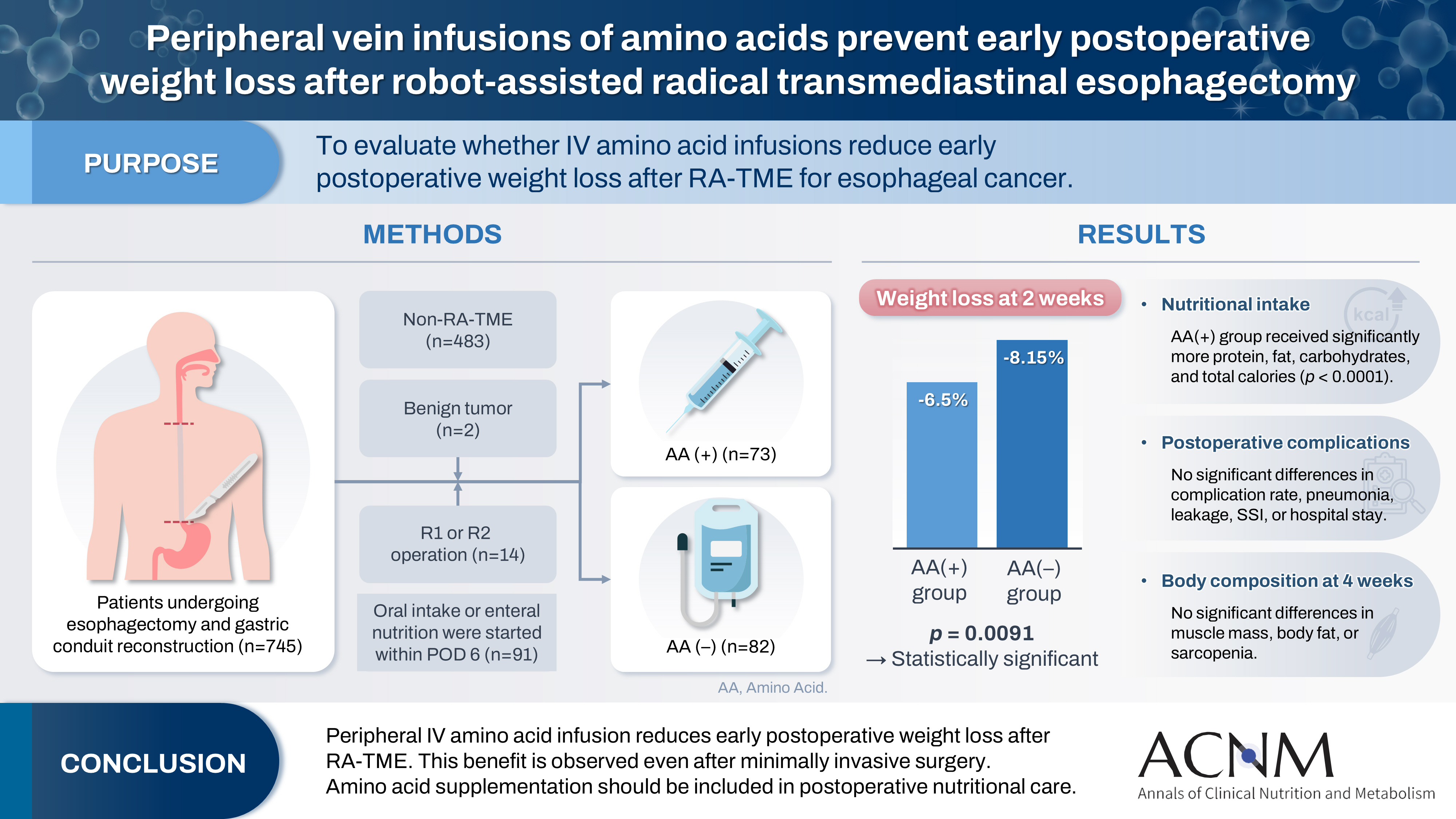
Postoperative body weight loss (PBWL) is linked to poor long-term outcomes following esophagectomy for esophageal cancer, making perioperative nutrition critically important. Although minimally invasive procedures such as robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy (RA-TME) have become more prevalent, less attention has been paid to perioperative nutritional management. This study evaluates the impact of intravenous (IV) amino acid infusions on PBWL in patients undergoing RA-TME.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 155 patients who underwent RA-TME for esophageal or esophagogastric junction cancer at our hospital between 2011 and 2022. Patients were divided into two groups: AA(+) (n=73, received IV amino acids between postoperative days 1–6) and AA(–) (n=82, did not receive IV amino acids). Oral or enteral nutrition was withheld until postoperative day 6. We compared nutrient intake, postoperative outcomes, and nutritional status between groups.
Results
Patient backgrounds, surgical outcomes, and complication rates were similar in both groups. However, the AA(+) group received significantly greater energy and nutrient intake. PBWL at 2 weeks post-surgery was significantly lower in the AA(+) group than in the AA(–) group (6.50% vs. 8.15%, P=0.0091).
Conclusion
IV amino acid infusion may help mitigate early PBWL after RA-TME.
- 1,335 View
- 17 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN First
First Prev
Prev


