-
Impact of tube feeding after pancreaticoduodenectomy on nutritional intake and status: a retrospective cohort study in Japan
-
Masaharu Ishida, Masahiro Iseki, Shuichiro Hayashi, Aya Noguchi, Hideaki Sato, Shingo Yoshimachi, Akiko Kusaka, Mitsuhiro Shimura, Shuichi Aoki, Daisuke Douchi, Takayuki Miura, Shimpei Maeda, Masamichi Mizuma, Kei Nakagawa, Takashi Kamei, Michiaki Unno
-
Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(3):203-209. Published online December 1, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0020
-
-
 Graphical Abstract Graphical Abstract
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
 - Purpose
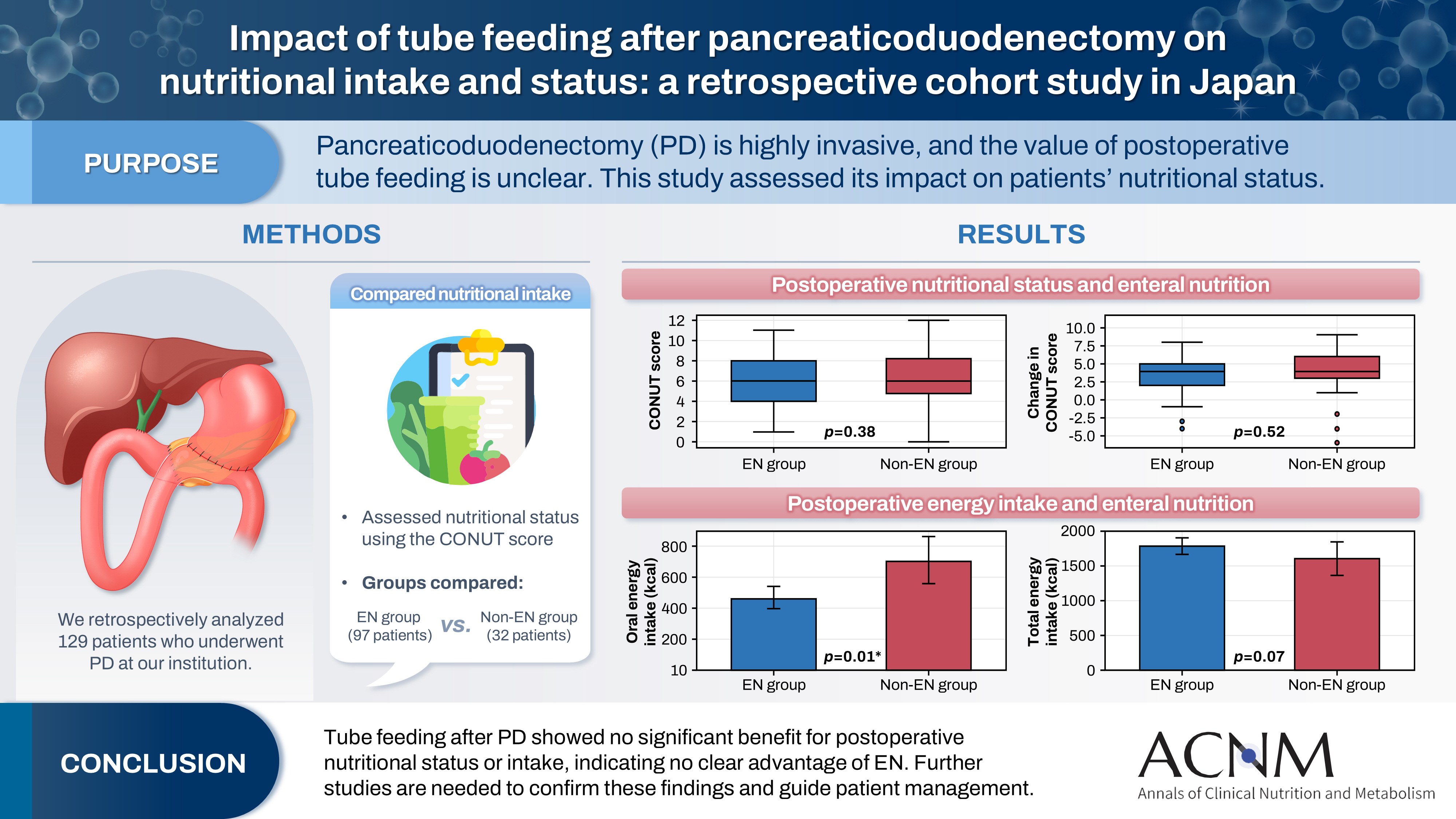
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) is one of the most invasive procedures in gastrointestinal surgery. However, the clinical significance of postoperative tube feeding remains unclear. This study investigated the impact of enteral nutrition (EN) on the postoperative nutritional status of patients undergoing PD.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 129 patients who underwent PD at Tohoku University Hospital. Nutritional intake and status, evaluated using the Controlling Nutritional Status score, were compared between two groups: an EN group (97 patients) and a non-EN group (32 patients).
Results
There were no significant differences between the two groups in age, sex, body mass index, underlying diseases, operative duration, blood loss, postoperative pancreatic fistula, postoperative complications, delayed gastric emptying, or length of hospital stay. Although the EN group showed improvements in nutritional status both at discharge and compared with preoperative values, none of these changes reached statistical significance. Oral caloric intake was significantly higher in the non-EN group (P=0.01). In contrast, total energy intake was higher in the EN group, but this difference did not reach statistical significance (P=0.07).
Conclusion
Tube feeding after PD did not significantly influence postoperative nutritional status or overall nutritional intake. These findings suggest that EN offers no clear advantage over other approaches; however, further research is warranted to validate these results, refine existing guidelines, and optimize postoperative patient management.
|







