-
Peripheral vein infusions of amino acids prevent early postoperative weight loss after robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy: a retrospective study in Japan
-
Tomonori Narita, Kazuhiko Fukatsu, Satoshi Murakoshi, Reo Inoue, Kenichi Kono, Midori Noguchi, Nana Matsumoto, Shoh Yajima, Koichi Yagi, Yoshifumi Baba
-
Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):149-155. Published online August 1, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0012
-
-
 Graphical Abstract Graphical Abstract
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
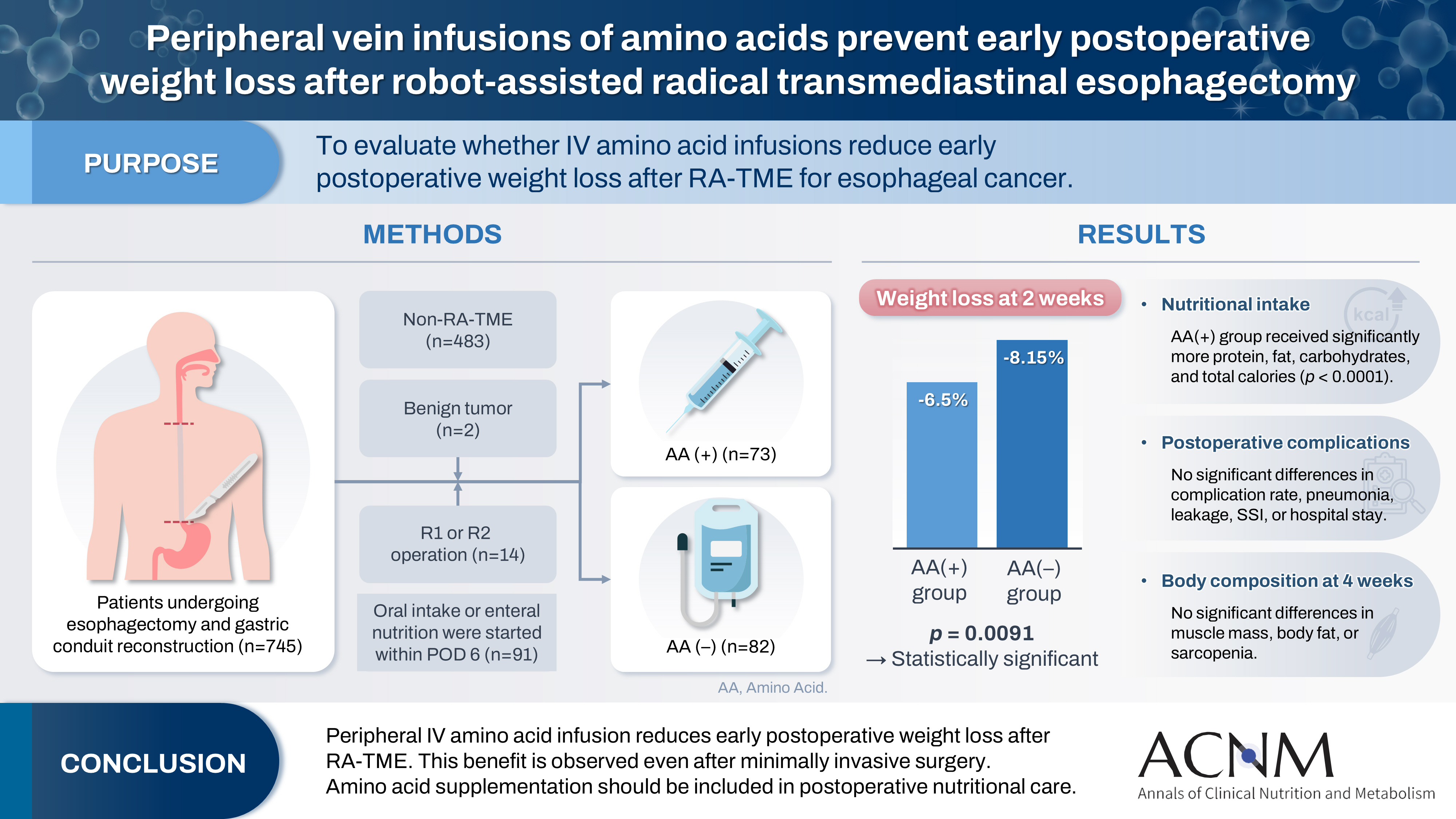 - Purpose
Postoperative body weight loss (PBWL) is linked to poor long-term outcomes following esophagectomy for esophageal cancer, making perioperative nutrition critically important. Although minimally invasive procedures such as robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy (RA-TME) have become more prevalent, less attention has been paid to perioperative nutritional management. This study evaluates the impact of intravenous (IV) amino acid infusions on PBWL in patients undergoing RA-TME.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 155 patients who underwent RA-TME for esophageal or esophagogastric junction cancer at our hospital between 2011 and 2022. Patients were divided into two groups: AA(+) (n=73, received IV amino acids between postoperative days 1–6) and AA(–) (n=82, did not receive IV amino acids). Oral or enteral nutrition was withheld until postoperative day 6. We compared nutrient intake, postoperative outcomes, and nutritional status between groups.
Results
Patient backgrounds, surgical outcomes, and complication rates were similar in both groups. However, the AA(+) group received significantly greater energy and nutrient intake. PBWL at 2 weeks post-surgery was significantly lower in the AA(+) group than in the AA(–) group (6.50% vs. 8.15%, P=0.0091).
Conclusion
IV amino acid infusion may help mitigate early PBWL after RA-TME.
-
Impact of postoperative nutritional status on the patients’ clinical outcomes and knee biomechanics following total knee arthroplasty in Japan: a prospective cohort study
-
Kenichi Kono, Tetsuya Tomita, Takaharu Yamazaki, Masashi Tamaki, Shuji Taketomi, Ryota Yamagami, Reo Inoue, Yuki Taniguchi, Sakae Tanaka, Kazuhiko Fukatsu
-
Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):50-57. Published online April 1, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.24.019
-
-
 Graphical Abstract Graphical Abstract
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
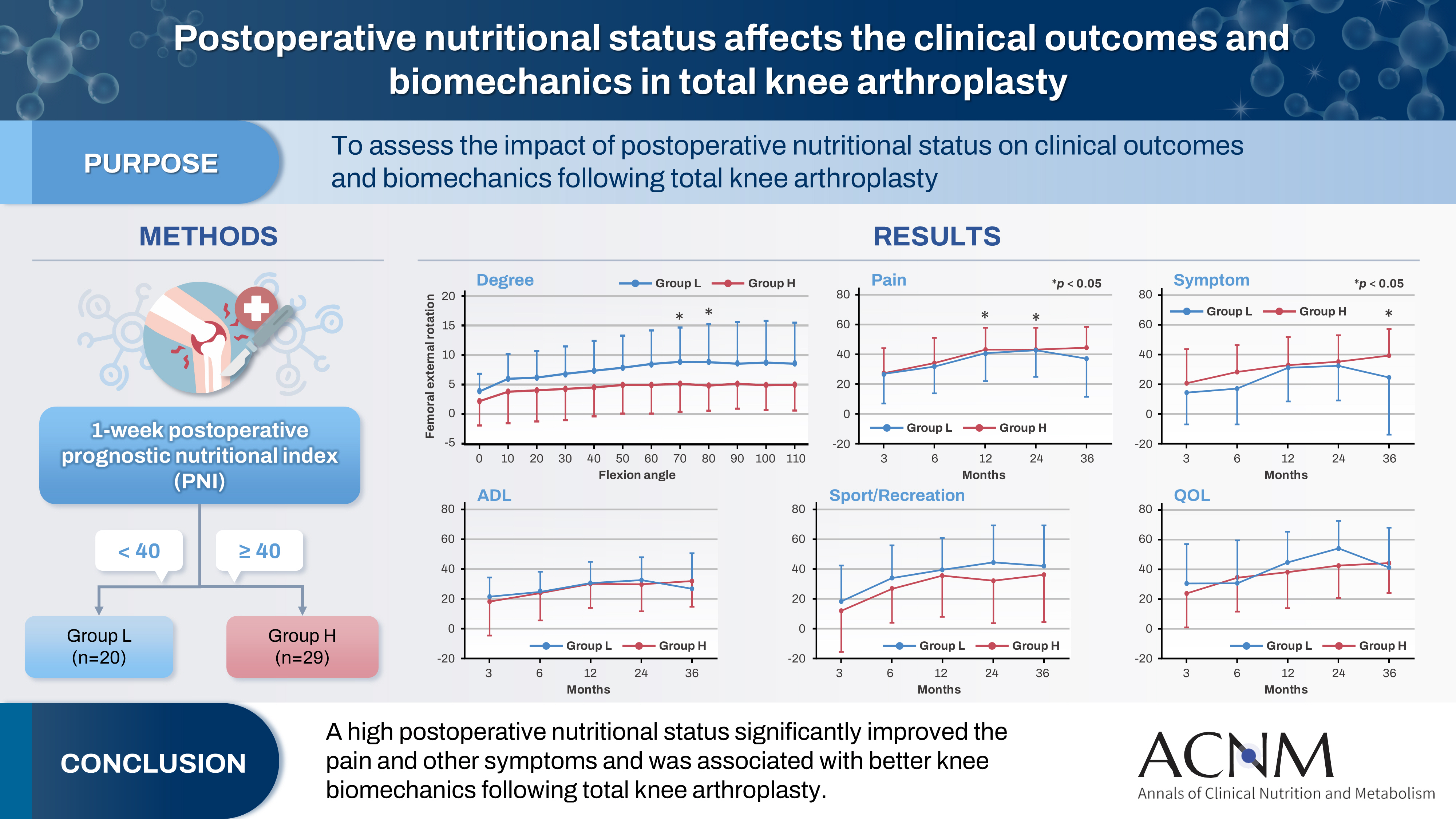 - Purpose
The impact of postoperative nutritional status on clinical outcomes and biomechanics following total knee arthroplasty remains largely unknown. This study aimed to assess this question using the prognostic nutritional index to evaluate the nutritional status of orthopedic participants.
Methods
Patients with knee osteoarthritis who underwent total knee arthroplasty (n=49) in Japan were divided into two groups based on their 1-week postoperative prognostic nutritional index. Group L patients had a prognostic nutritional index <40, whereas Group H comprised patients with a prognostic nutritional index ≥40. Postoperative improvements in Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score were evaluated. The patients performed squats under single-fluoroscopic surveillance in the sagittal plane for biomechanical evaluation. A two-dimensional/three-dimensional registration technique was employed to measure the tibiofemoral kinematics. The axial rotation of the femoral component relative to the tibial component and the anteroposterior translation of the medial and lateral femorotibial contact points were measured.
Results
Group H showed significantly higher pain scores than Group L at 12 and 36 months postoperatively and a significantly higher symptom score at 36 months postoperatively. The kinematic comparison revealed that the axial external rotation in Group L was larger than that in Group H from 70° to 80° with flexion. Moreover, in the medial anteroposterior translation, Group L was more anteriorly located than Group H, with flexion beyond 30°.
Conclusion
The results suggest that a high postoperative nutritional status significantly improved pain and other symptoms and was associated with better knee biomechanics following total knee arthroplasty.
-
Association of soy oil-based lipid injectable emulsion with early body weight loss after minimally invasive esophagectomy in Japan: a retrospective cohort study
-
Tomonori Narita, Kazuhiko Fukatsu, Kenichi Kono, Satoshi Murakoshi, Reo Inoue, Midori Noguchi, Nana Matsumoto, Shoh Yajima, Koichi Yagi, Yoshifumi Baba
-
Received August 13, 2025 Accepted January 12, 2026 Published online February 23, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0030
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
- Purpose
Postoperative body weight loss (PBWL) is associated with poor long-term outcomes following esophagectomy for esophageal cancer, underscoring the critical importance of perioperative nutritional management. Although minimally invasive procedures, such as robot-assisted radical transmediastinal esophagectomy (RA-TME), have become increasingly prevalent, perioperative nutritional strategies have received comparatively limited attention. This study evaluated the impact of soy oil-based lipid injectable emulsion (SO-ILE) on PBWL in patients undergoing RA-TME.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 155 patients who underwent RA-TME for esophageal or esophagogastric junction cancer at our hospital between 2011 and 2022. Patients were divided into two groups: the lipid (+) group (n=33), which received SO-ILE between postoperative days 1 and 6, and the lipid (–) group (n=122), which did not receive SO-ILE. Oral or enteral nutrition was withheld until postoperative day 6. Nutrient intake, postoperative outcomes, and nutritional status were compared between the two groups.
Results
Patient backgrounds, surgical outcomes, and postoperative complication rates were similar between the two groups. However, patients in the lipid (+) group received significantly greater total energy and nutrient intake. PBWL at 2 weeks after surgery was significantly lower in the lipid (+) group than in the lipid (–) group (5.8% vs. 7.4%; P=0.027). Multivariable analysis showed that absence of SO-ILE administration was the only significant risk factor for PBWL greater than 5% at 2 weeks after RA-TME (P=0.038).
Conclusion
SO-ILE may have the potential to mitigate early PBWL after RA-TME.
|













