Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Current practices and challenges in nutrition support team activities, 2025 in Korea: a multicenter cross-sectional descriptive study
- So Hyun Nam
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):97-103. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0026
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the current practices, activities, and challenges of nutrition support teams (NSTs) in Korea. The assessment was conducted as part of the 4th NST Leadership Program of the Korean Society of Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition held in 2025, which seeks to foster leadership and enhance team functionality.
Methods
A nationwide survey was conducted in February 2025 among 54 NST members from 44 institutions. The survey explored team composition, consultation volume, educational programs, barriers to implementation, institutional support, and reimbursement challenges.
Results
Of the 44 participating hospitals, most (86.4%) operated a single NST, with multidisciplinary physician involvement from over three specialties in 77.2% of cases. Inpatient referrals to NSTs were generally low, with less than 10% at 63% of institutions. Only 40.9% had an individual office, and formal incentive systems were reported in 18.1% of hospitals. Educational programs for in-hospital staff were limited (29.5%), and less than half conducted regular academic meetings. Rates of adoption of NST recommendations varied widely, with barriers including a lack of engagement from attending physicians, failure to review the recommendations, and department-specific clinical policies. Efforts to promote NST activation included computerized prescription systems, automated referral workflows, staff education, and quality improvement initiatives. Participants focused on sharing effective NST cases, building incentives, exchanging clinical insights, clarifying team roles and leadership, and developing unified practice guidelines.
Conclusion
NSTs in Korea are well established but face ongoing challenges in collaboration and sustainability. Continued leadership and policy support are crucial for enhancing team performance and improving patient outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Perioperative nutritional practices and pediatric nutrition support team implementation in Korea: a cross-sectional study
Dayoung Ko, Honam Hwang, Hee-Beom Yang, Joong Kee Youn, Hyun-Young Kim
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(3): 181. CrossRef
- Perioperative nutritional practices and pediatric nutrition support team implementation in Korea: a cross-sectional study
- 4,826 View
- 72 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Development of a Japanese version of the Short Bowel Syndrome-Quality of Life (SBS-QoL) scale
- Yuko Tazuke, Mayu Suzuki, Sae Kikuchi, Kaori Ishiguro, Hiroomi Okuyama
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):132-138. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0016
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
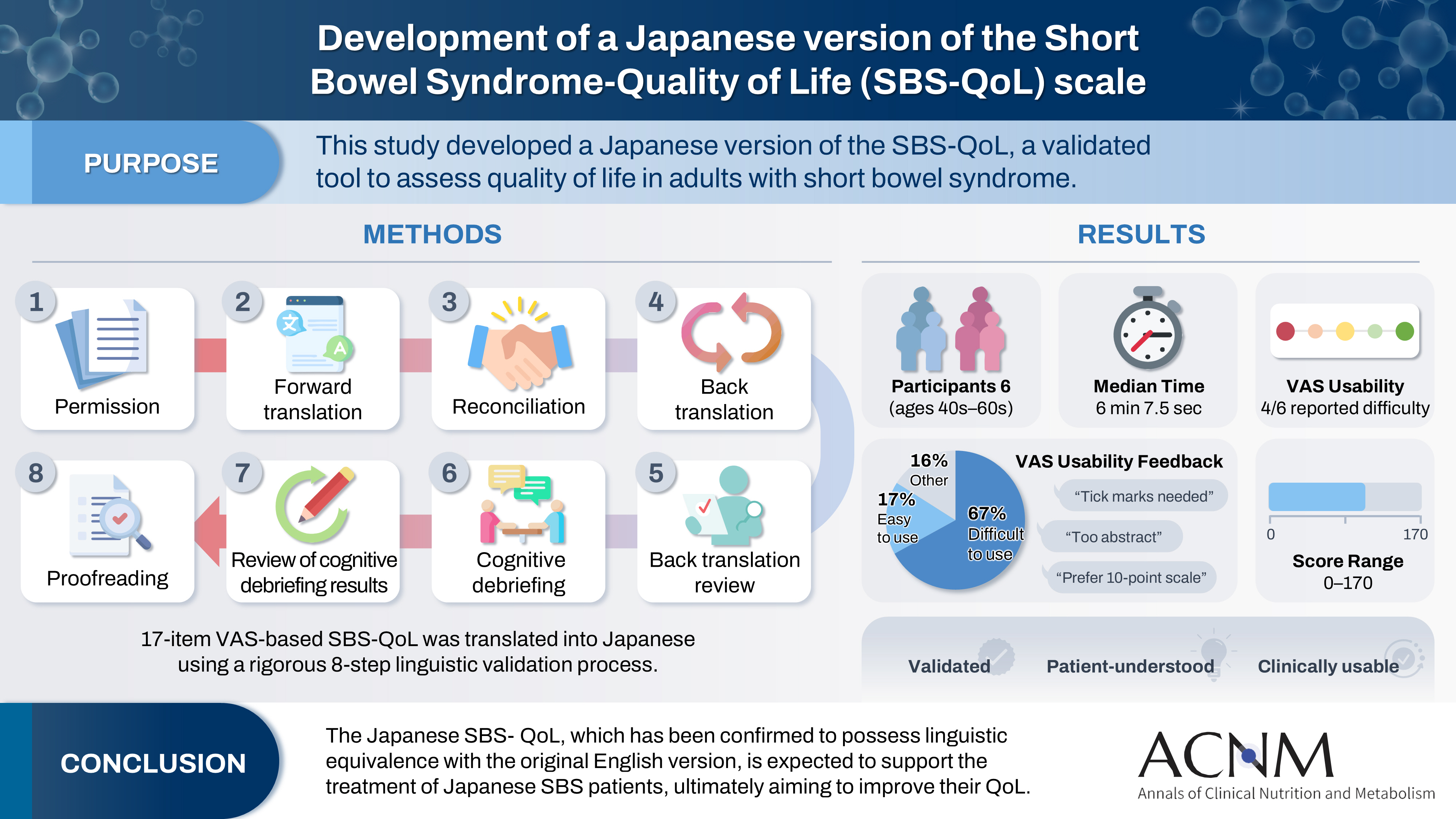
- Purpose
The Short Bowel Syndrome‐Quality of Life (SBS‐QoL) scale is a reliable and sensitive instrument developed to measure and evaluate the quality of life (QoL) in adult patients with short bowel syndrome (SBS). In Japan, increasing attention has been given to the assessment of QoL in patients with SBS; however, no Japanese‐language SBS‐specific scale is currently available. This study aimed to develop a Japanese version of the SBS‐QoL based on the original English version.
Methods
A provisional Japanese version was created in accordance with the guidelines of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research (ISPOR) Task Force, utilizing a process of forward translation, adjustment, and back translation.
Results
Cognitive debriefing using the provisional Japanese version was conducted with six Japanese patients with SBS. Based on these results, the Japanese wording was evaluated and revised, leading to the creation of the final Japanese version.
Conclusion
The Japanese SBS‐QoL, which has been confirmed to possess linguistic equivalence with the original English version, is expected to support the treatment of Japanese SBS patients, ultimately aiming to improve their QoL.
- 1,447 View
- 19 Download

- Dysphagia and quality of life: a narrative review
- Jung Mi Song
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(2):43-48. Published online August 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.2.43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: Dysphagia is a chronic health condition that causes impairment of eating and drinking functions. It occurs in various diseases such as stroke, neurodegenerative disease, brain tumor, and head and neck cancer, and can also occur during the normal aging process.
Current concept: As patients experience symptoms of dysphagia, they no longer feel the pleasure of eating, depression and anxiety increase, and self-esteem decreases. Prolonged loss of appetite can lead to malnutrition, which can lead to death due to serious complications such as aspiration pneumonia and airway obstruction. Dysphagia reduces quality of life by affecting basic activities of daily living, limitations in social life, nutritional deficiencies, and mood disorders.
Conclusion: Accordingly, I plan to conduct a literature review on the quality of life of patients with dysphagia. First, to determine the relationship between quality of life and sociodemographic, physical health, and mental health characteristics of patients with dysphagia. I also aim to review quality of life measurement tools and intervention programs for patients with dysphagia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidence and Risk Factors of Dysphagia After Cardiac Surgery: A Scoping Review
Christos Kourek, Vania Labropoulou, Emilia Michou, Stavros Dimopoulos
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(12): 4279. CrossRef - Psychometric Properties of the Spanish Version of the Swallowing Quality of Life Questionnaire in Fibromyalgia Patients
Irene Calles-Plata, Araceli Ortiz-Rubio, Laura Pérez-Gisbert, Irene Torres-Sánchez, Andrés Calvache-Mateos, Marie Carmen Valenza, Alejandro Heredia-Ciuró
Healthcare.2025; 13(22): 2948. CrossRef - Association Between Swallowing Dysfunction and Multidimensional Quality of Life Among Community-Dwelling Healthy Korean Older Adults: A Pilot Cross-Sectional Study
Hyun-Ah Jang, Jun-Seon Choi
Healthcare.2025; 13(22): 2964. CrossRef
- Incidence and Risk Factors of Dysphagia After Cardiac Surgery: A Scoping Review
- 14,283 View
- 272 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Efficacy of high-protein diet protocol and education after distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer patients to prevent loss of lean body mass in Korea: a non-randomized controlled study
- Hee Kyung Yoon, Sun Ae Kim, Ji Yoon Han, Dong Jin Kim
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(1):10-19. Published online April 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.1.10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose: We studied whether active education of patients about the importance of a high-protein diet can prevent lean body mass loss after gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Methods: In the study group, intensive high protein diet education and monitoring was performed immediate post operative, 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery. Study group patients were compared with data from the control group formed using propensity matching with the study group for age, sex, resection extent, and TNM stage. Clinicopathologic factors were compared between the groups, and changes in quality of life (QOL) and lean body mass between preoperative levels and 6 months after surgery were assessed.
Results: Among the 100 patients, 31 patients from each group were matched with propensity matching. The groups had no significant clinicopathologic differences. Although the changes in QOL scale and body composition did not differ statistically between the groups, a favorable trend was observed in the study group. Six months after surgery, the mean change in the QOL scale, which measured physical, role, emotional, cognitive, and social functioning, decreased less than the control group or even increased in the study group. In the body composition analysis, the study group showed greater reductions in weight, body mass index, fat mass, and body fat percentage than the control group, and their lean body mass and skeletal muscle mass decreased less.
Conclusion: A high-protein diet protocol and education might increase patient QOL and prevent a decrease in lean body weight 6 months after distal gastric resection.
- 4,060 View
- 40 Download

- Development of the Korean Version of the Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index Questionnaire
- In Jun Yang, Heung-Kwon Oh, Jeehye Lee, Jung Wook Suh, Hong-min Ahn, Hyeonjeong Park, Hyun Hee Sim, Yong Beom Cho, In Kyu Lee, Seungbum Ryoo, Dong-Won Lee, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2022;14(1):32-37. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2022.14.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: To establish a standardized quality of life measurement that allows global cross-study comparisons, we translated the Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index (GIQLI) into Korean and linguistically validated the Korean version of the GIQLI (K-GIQLI) in patients who underwent colorectal surgery.
Materials and Methods: A cross-cultural adaptation of the original GIQLI was created based on the established guidelines. Based on participation in a cognitive interview, 20 patients with colorectal cancer were enrolled in the study. To ensure that the Korean version of the questionnaire was understood as intended, the time needed to complete the questionnaire was measured, and three additional items related to comprehension were added.
Results: From May to July 2021, two translators, whose native language was Korean translated the GIQLI items into Korean, and a native English editor who had no knowledge of the original questionnaire translated the items back into English. In the cognitive interview, the median age of the patients was 61.8 (range: 44~82) years, and the median time required to complete the questionnaire was 6.5 (range: 5~10) min. For the language and cultural adaptation process, the participants’ comprehension of the questionnaire was measured on a scale of 1~5, with a mean score of 4 (range: 3~4).
Conclusion: The K-GIQLI was developed and did not exhibit a significant difference from the original English version in terms of social, linguistic, and cultural differences between the Western world and Republic of Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Longitudinal quality of life assessment after laparoscopic colorectal cancer surgery using the Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index questionnaire: A multicentre prospective study
Tae‐Gyun Lee, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Heung‐Kwon Oh, Yong Beom Cho, Chang Hyun Kim, Ju Hyun Lee, Hong‐Min Ahn, Hye‐Rim Shin, Mi Jeong Choi, Min Hyeong Jo, Duck‐Woo Kim, Sung‐Bum Kang
Colorectal Disease.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of laparoscopic and robotic surgery of choledochal cyst in pediatrics: single center experience
Jiyong Jang, Dayoung Ko, Joong Kee Youn, Hee-Beom Yang, Hyun-Young Kim
Surgical Endoscopy.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Longitudinal quality of life assessment after laparoscopic colorectal cancer surgery using the Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index questionnaire: A multicentre prospective study
- 1,904 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Longitudinal Change in Health-Related Quality of Life after Total Gastrectomy: Approach Based on the Minimally Important Difference
- Sang Chun Park, Oh Jeong, Ji Hoon Kang, Mi Ran Jung
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2021;13(2):43-51. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2021.13.2.43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: The post-operative quality of life (QoL) is a significant concern for patients undergoing gastrectomy. Unlike subtotal gastrectomy, the detailed aspects of QoL involving the ability to perform everyday activities that reflect physical, psychological, and social well-being; and satisfaction with levels of functioning and control of the disease after total gastrectomy remain poorly investigated.
Materials and Methods: We enrolled 170 patients who underwent total gastrectomy for gastric carcinoma and completed the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality-of-Life questionnaires (QLQ) C30 and STO22 preoperatively and post-operatively at 1, 6, and 12 months. We investigated the QoL change in terms of the minimally important difference (MID), which refers to a score change patients would perceive as clinically important (effect size >0.5).
Results: At 1-month post-surgery, MID in global health, physical, social, role, emotional, and cognitive functions was observed at 44.0%, 68.0%, 42.7%, 38.7%, 32.0%, and 16.0% respectively. Of QLQ-C30 symptoms, MID was frequently observed in appetite (52.9%). Of the QLQ-STO22 symptoms, MID was frequently observed in eating restrictions (74.1%), dysphagia (63.5%), pain (51.8%), and anxiety (50.6%). At 12 months post-surgery, MID in global health, physical, role, cognitive, social, and emotional functions was 32.9%, 58.8%, 42.4%, 40.0%, 36.5%, and 17.6%, respectively. Of QLQ-C30 symptoms, MID was frequently observed in diarrhea (52.9%). Of the QLQ-STO22 symptoms, MID was frequently observed in eating restrictions (63.5%), dysphagia (52.9%), body image (55.3%), pain (55.3%), and anxiety (51.8%). Male sex, comorbidity, D2 lymphadenectomy, and post-operative morbidity were associated with MID in global health at 12 months post-surgery.
Conclusion: This study provides information about the detailed aspects of impairment in various functions and symptoms of QoL after total gastrectomy. This information can be used to develop a tailor-made management plan for QoL. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experiences After Endoscopic Resection in Patients With Early Gastric Cancer in Korea: A Qualitative Study
Yoon Kyung Kim, Chun-Ja Kim, Eunyoung Park, Ji Yea Lee, Kee-Myung Lee, Elizabeth A. Schlenk
Journal of Transcultural Nursing.2025; 36(5): 593. CrossRef - Proximal gastrectomy with tubular stomach reconstruction vs total gastrectomy for proximal gastric cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A multicenter retrospective study
Yi-Ming Lu, Peng Jin, Hai-Kuo Wang, Xin-Xin Shao, Hai-Tao Hu, Yu-Juan Jiang, Wang-Yao Li, Yan-Tao Tian
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Experiences After Endoscopic Resection in Patients With Early Gastric Cancer in Korea: A Qualitative Study
- 2,566 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of Nutritional Intervention by the Nutrition Support Team on Postnatal Growth in Preterm Infants
- So Jin Yoon, Joo Hee Lim, Soon Min Lee, Sun Jung Kim, Sun Kyung Lee, Soo Min Lee
- J Clin Nutr 2020;12(2):26-33. Published online December 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/jcn.2020.12.2.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: Nutritional intervention by an interdisciplinary nutrition support team (NST) can potentially improve postnatal growth outcomes in preterm infants. This study aimed to measure the growth impact of a nutritional intervention package performed by an NST in a quality improvement effort in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Methods: Fifty-two infants born below 2,000 g and admitted to NICU participated in the Quality Improvement (QI) program between March 2016 and February 2017. The nutritional intervention was applied according to newly established nutritional guidelines on parenteral and enteral nutrition, and an NST performed a weekly nutritional assessment. The Z-scores of weight, height, and head circumference were calculated according to the gestational age and sex. The clinical impact on postnatal growth was compared between the QI and pre-QI groups. The pre-QI group included 69 infants admitted in the same NICU between 2014 and 2015.
Results: The time to the initiation of enteral nutrition decreased significantly (P<0.001). Changes in weight (P=0.027), head circumference (P=0.003), Z-scores between birth, and 40 weeks postconceptional age (PCA) were significantly larger in the QI than the pre-QI group. The percentage of infants weighing below the 10th percentile at one month after birth and at 40 weeks PCA was higher in the pre-QI than the QI group.
Conclusion: The implementation of evidence-based best practices for preterm nutrition resulted in significant improvements in the growth outcomes in preterm infants. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition Supply and Growth Post Nutrition Support Team Activity in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Hye Min Ha, Yu Jin Jung, Yoo Rha Hong, So Yoon Choi
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition.2024; 27(5): 313. CrossRef
- Nutrition Supply and Growth Post Nutrition Support Team Activity in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- 989 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Present and Future of Nutrition Support Team
- Ji-Young Sul, Jeong Goo Kim
- Surg Metab Nutr 2019;10(1):1-4. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2019.10.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Now days, the use of specialized nutrition support has become a standard tool in the care of patients. With the development of specialized nutrition support, an interdisciplinary approach was essential to archive a goal. Fortunately, Nutritional support team (NST) consultation fee has been reimbursed under the national health insurance system since 2014. Overall, it might be true that there has been some progress in the NST’s activities. However, it is still questionable whether there was a positive effect in terms of quality or cost effectiveness compared to quantitative improvements. Before taking into consideration of the future of NST, we are going to look at the status of nutritional support practice and utility of NST in Korea. Upon this background, we hope to make constructive suggestions for a better future of NST.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current practices and challenges in nutrition support team activities, 2025 in Korea: a multicenter cross-sectional descriptive study
So Hyun Nam
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 97. CrossRef - Factors affecting target caloric achievement and calorie intake improvement: the nutrition support team's role
Jeong Bin Bong, So-Yeong Kim, Han Uk Ryu, Hyun Goo Kang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identifying the nutrition support nurses’ tasks using importance–performance analysis in Korea: a descriptive study
Jeong Yun Park
Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions.2023; 20: 3. CrossRef
- Current practices and challenges in nutrition support team activities, 2025 in Korea: a multicenter cross-sectional descriptive study
- 799 View
- 10 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Analysis of Compliance with Plan of Nutritional Support Team in Intensive Care Unit
- Eunkyoung Kim, Jingyeong Kim, YunJu Park, Soyoung Baek, JinJu Lee, AeHee Lee, Jae Im Lee, Chang Hyeok An, Maru Kim
- Surg Metab Nutr 2016;7(2):29-31. Published online December 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2016.7.2.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose:
To improve the nutritional state of patients, cooperation between medical and nutritional support teams is needed. The present study analyzed compliance with the plan of the nutritional support team.
Materials and Methods:
From September 2015 to February 2016, patients undergoing consultation with the nutritional support team at an intensive care unit was enrolled in the study. Their medical records were retrospectively reviewed.
Results:
A total of 123 patients were analyzed. Overall compliance was 56.9% (70/123). Main reason of the non-compliant group was change in patient’s condition (44/53).
Conclusion:
To improve compliance with the medical team, there is a need to assess patients’ condition more rapidly.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutritional Status of Intensive Care Unit Patients According to the Referral to the Nutrition Support Team and Compliance with the Recommendations
Yunjin Sohn, Taisun Hyun
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2022; 27(2): 121. CrossRef
- Nutritional Status of Intensive Care Unit Patients According to the Referral to the Nutrition Support Team and Compliance with the Recommendations
- 720 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Economic Evaluation of Home Total Parenteral Nutrition
- Ja Kyung Min
- J Clin Nutr 2016;8(1):19-23. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/jcn.2016.8.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The restricted resources on healthcare highlights the importance of clinical and cost effectiveness. The social and economic costs of chronic diseases are increasing. Home total parenteral nutrition (home TPN) for the patients with intestinal failure is a life-sustaining therapy until intestinal transplantation. An economic evaluation of home TPN has not been conducted in Korea. Three types of economic evaluations for home TPN are cost benefit analysis, cost effectiveness analysis, and cost utility analysis. Korea’s medical market is competitive due to the limited health care resources. A health care delivery system from hospital to home needs to be established under the supervision of professional Nutrition Support Team staff including the systematic policies and social recognition.
- 756 View
- 1 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev


