Scopus, KCI, KoreaMed

Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
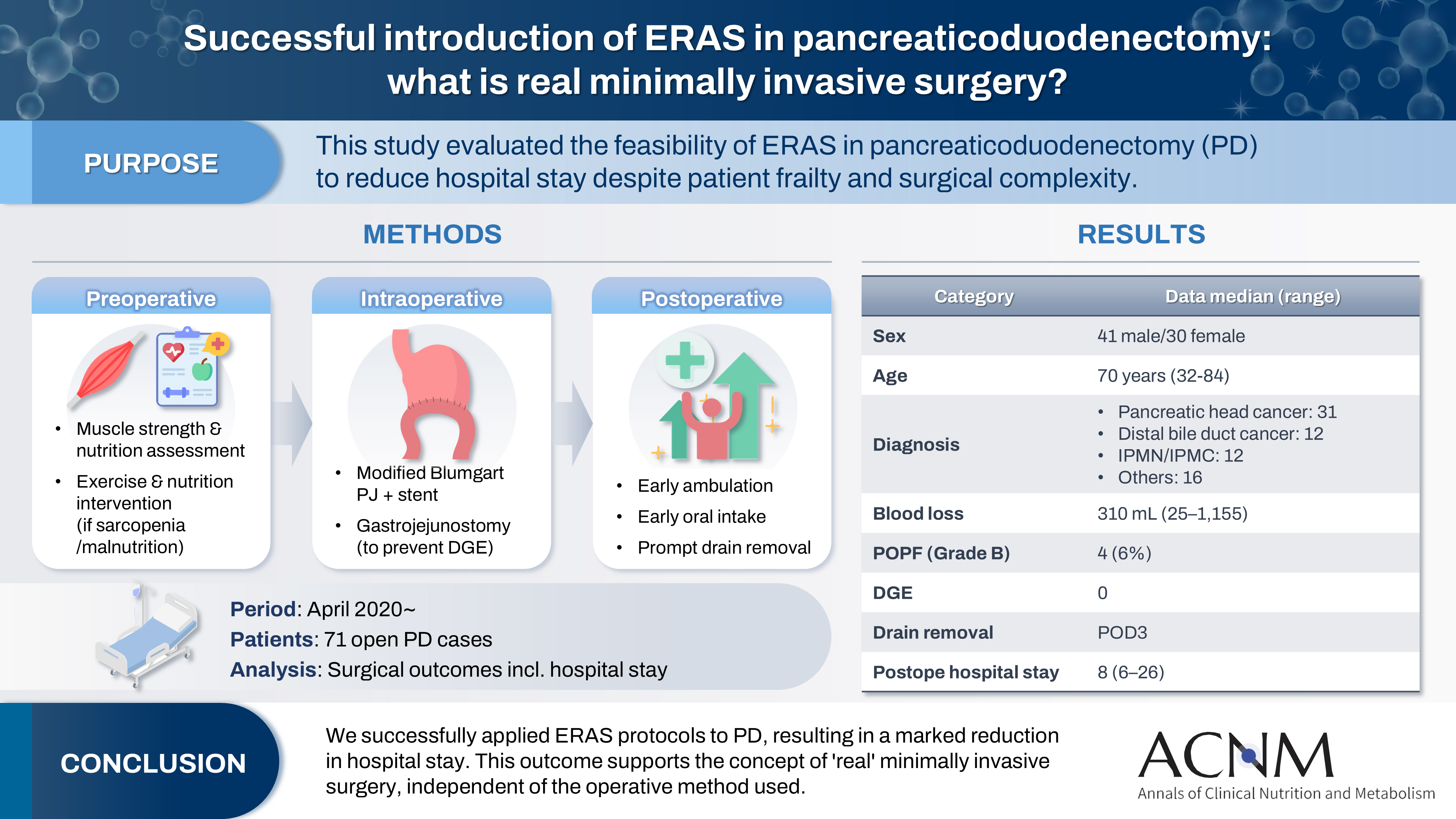
- Successful introduction of ERAS in pancreaticoduodenectomy: what is real minimally invasive surgery?
- Toshimi Kaido, Yosuke Miyachi, Koichiro Mitsuoka, Mariko Sambommatsu
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(2):156-161. Published online August 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0014
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 
- Purpose
The introduction of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols for pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) has been considered challenging due to factors such as preexisting malnutrition, sarcopenia, the complexity of the surgery, and the high incidence of postoperative complications, including postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) and delayed gastric emptying (DGE). This study aimed to determine whether ERAS could be implemented in PD to achieve shorter postoperative hospital stays.
Methods
Our novel approach consists of three components. Preoperatively, we routinely assess patients' muscle strength and nutritional status and initiate exercise and nutritional interventions for those identified with sarcopenia or malnutrition. Intraoperatively, we perform pancreaticojejunostomy using a modified Blumgart’s technique with our stent placement policy and utilize new gastrojejunostomy methods to prevent DGE. Principles of postoperative management are early ambulation, early oral intake, and early drain removal. Since April 2020, we have employed this strategy and retrospectively evaluated its effectiveness. We enrolled 71 consecutive patients who underwent open PD with curative intent. Various surgical outcomes, including postoperative hospital stay, were analyzed.
Results
There were 41 men and 30 women, with a median age of 70 years. Preoperative diagnoses included pancreatic head cancer in 31, distal bile duct cancer in 12, and others. Median intraoperative blood loss was 310 mL. Grade B POPF occurred in four patients (6%). No cases of DGE were observed. The median postoperative hospital stay was 8 days (range, 6–26 days).
Conclusion
We successfully implemented ERAS protocols in PD and achieved a significantly reduced postoperative hospital stay. We propose that this approach is “real minimally invasive surgery," regardless of the surgical technique used.
- 3,966 View
- 19 Download

- Perioperative nutritional management to improve long-term outcomes in critically ill perioperative organ transplant patients: a narrative review
- Toshimi Kaido
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2025;17(1):18-24. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.25.0005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This review examines the significance of perioperative nutritional management in organ transplantation, with a particular focus on liver transplantation. Organ transplant recipients often experience malnutrition and sarcopenia due to nutritional and metabolic abnormalities associated with organ dysfunction. Because transplantation is a highly invasive procedure, optimizing perioperative nutritional care is critical for improving short-term outcomes and reducing postoperative infection-related mortality.
Current concept
Recent clinical investigations have shown that liver transplant recipients, who are frequently afflicted with end-stage liver disease and uncompensated cirrhosis, are particularly vulnerable to protein-energy malnutrition and secondary sarcopenia. Our analysis identified low pre-transplant nutritional status and the absence of preoperative branched-chain amino acid supplementation as independent risk factors for post-transplant sepsis. In response, we developed a customized nutritional therapy protocol that incorporates precise body composition analysis, serial measurements of biochemical markers (including prealbumin, zinc, and the branched-chain amino acid/tyrosine ratio), and targeted supplementation with branched-chain amino acids, zinc acetate, and synbiotics. Early initiation of enteral nutrition coupled with postoperative rehabilitative interventions resulted in improved outcomes. In addition, stratified body composition parameters correlated with survival differences and informed revised transplantation criteria.
Conclusion
Tailored perioperative nutritional management and rehabilitative strategies are essential for improving early postoperative outcomes in liver transplantation. These findings underscore the need for proactive nutritional assessment and intervention, which may represent a breakthrough in transplant prognosis. Future research should refine nutritional protocols and integrate novel biomarkers, while education and interdisciplinary collaboration remain crucial for enhancing transplant outcomes and reducing complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
Ye Rim Chang
Ann Clin Nutr Metab.2025; 17(2): 95. CrossRef
- Strengthening collaboration: introducing the contributions of Japanese Society for Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition to Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism
- 4,356 View
- 108 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Incidence and risk factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease after pancreaticoduodenectomy in Korea: a multicenter retrospective cohort study
- Chang-Sup Lim, Hongbeom Kim, In Woong Han, Won-Gun Yun, Eunchae Go, Jaewon Lee, Kyung Chul Yoon, So Jeong Yoon, Sang Hyun Shin, Jin Seok Heo, Yong Chan Shin, Woohyun Jung
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(3):125-133. Published online December 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the incidence, risk factors, and clinical course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) following pancreaticoduodenectomy, focusing on the role of adjuvant chemotherapy and other metabolic changes.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 189 patients who underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy between 2013 and 2016. NAFLD was diagnosed using computed tomography (CT) imaging, defined as a liver-to-spleen attenuation ratio <0.9. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity were assessed using preoperative CT scans. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify risk factors for NAFLD development.
Results: The cumulative incidence of NAFLD increased over time, with rates of 15.9% at one year, 20.4% at three years, and 35.2% at five years post-pancreaticoduodenectomy. Adjuvant chemotherapy was identified as the only significant independent predictor of NAFLD development (odds ratio, 2.74; 95% confidence interval, 1.16-6.70; P=0.023). No significant associations were found between NAFLD and pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT), sarcopenia, or sarcopenic obesity. Serial analysis of NAFLD status in long-term survivors revealed dynamic changes, with some patients experiencing spontaneous remission or recurrence.
Conclusion: NAFLD is a common, progressive complication following pancreaticoduodenectomy, particularly in patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Although no significant associations with PERT or sarcopenia were observed, these areas warrant further investigation. Long-term monitoring and targeted management strategies are recommended to address NAFLD in this population. Future prospective studies are needed to elucidate the natural history and contributing factors of NAFLD after pancreaticoduodenectomy.
- 3,662 View
- 61 Download

- Prognostic significance of serum creatinine and sarcopenia for 5-year overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer in Korea: a comparative study
- Jiahn Choi, Hye Sun Lee, Jeonghyun Kang
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(2):66-77. Published online August 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.2.66
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Purpose: Previous studies have demonstrated that the serum creatinine level and skeletal muscle index (SMI) (correlated with the overall survival [OS] of patients with colorectal cancer [CRC]). However, the combined significance of these 2 factors is not fully understood. The goal of this study was to investigate the prognostic potential of the combination of these two factors in patients with CRC.
Methods: The patients were categorized into subgroups based on preoperative serum creatinine level, with a cut-off value of 1.01 mg/dL for males and 0.80 mg/dL for females. The patients were further categorized into 4 groups based on SMI. Data were analyzed using the Cox proportional hazards model and Harrell’s concordance index (C-index).
Results: Poor 5-year OS was observed in patients with high SMI and high serum creatinine levels (hazard ratio [HR]=1.676, 95% confidence interval [CI]=1.110–2.529, P=0.013), low SMI and low serum creatinine levels (HR=1.916, 95% CI=1.249–2.938, P=0.002), and low SMI and high serum creatinine levels (HR=2.172, 95% CI=1.279–3.687, P=0.004) compared to those of patients with high SMI and low serum creatinine levels. Grouping patients based on both SMI and serum creatinine levels led to improved prognostic stratification (C-index, 0.626; 95% CI=0.587–0.666) compared to grouping based on SMI (CI difference=0.062, 95% CI=0.031–0.103, P=0.0011) or serum creatinine (CI difference=0.043, 95% CI=0.017–0.081, P=0.0072) alone.
Conclusion: Incorporating both SMI and serum creatinine levels enhances the prognostic stratification for 5-year OS in patients with CRC, surpassing the prognostic power of grouping solely based on SMI or creatinine.
- 3,275 View
- 18 Download

- Definition, assessments, and current research on sarcopenia in children: a narrative review
- Min-Jung Bang
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2024;16(2):49-56. Published online August 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2024.16.2.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: Sarcopenia is a well-established prognostic factor for the clinical outcomes of adult patients with cancer and chronic diseases and correlates with increased intensive care unit admissions and prolonged hospital stays. However, research on sarcopenia in children is limited due to its undefined criteria and a lack of studies exploring its impact on clinical outcomes.
Current concept: The challenges in pediatric sarcopenia research include the absence of standardized body composition methods to quantify muscle mass and muscular function, as well as inconsistencies in definitions. Additionally, there is a lack of age- and gender-specific normative data, particularly for young children and infants. Most studies also lack assessments of muscle function, which can lead to bias and misclassification of sarcopenia. The field is further hindered by poor study quality, limited outcome-focused research, and a dearth of longitudinal data. While some studies suggest that various diseases can affect children’s lean muscle mass, few have linked changes in muscle mass to clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: The existing literature on pediatric sarcopenia and its relationship with medical and surgical outcomes is sparse and indicates poorer outcomes associated with sarcopenia. Although extensive research has established a link between sarcopenia and adverse outcomes in adults, information on its impact in pediatric populations remains scarce. Further studies are needed to elucidate the association between muscle mass and outcomes in pediatric surgical patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Newer Insights on the Occurrence of Sarcopenia in Pediatric Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Past 5 Years of Literature
Georgios Kiosis, Despoina Ioannou, Kanellos Skourtsidis, Vasilis Fouskas, Konstantinos Stergiou, Dimitrios Kavvadas, Theodora Papamitsou, Sofia Karachrysafi, Maria Kourti
Cancers.2025; 17(19): 3188. CrossRef
- Newer Insights on the Occurrence of Sarcopenia in Pediatric Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Past 5 Years of Literature
- 4,227 View
- 91 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Liver Cirrhosis and Sarcopenia
- Hye Yeon Chon, Tae Hee Lee
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2022;14(1):2-9. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2022.14.1.2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Malnutrition is one of the most common complications in patients with liver cirrhosis. In previous studies, cirrhotic patients with severe malnutrition have been associated with higher morbidity and mortality rates before and after liver transplantation. Frailty and sarcopenia are phenotypes of severe malnutrition that have been associated with complications requiring hospitalization or mortality during the wait for transplantation in patients with cirrhosis. Tools for evaluating frailty include the Activities of Daily Living scale, the Karnofsky Performance Status scale, and the Liver Frailty Index. Diagnosed by using computed tomography, sarcopenia is measured with the skeletal muscle index at L3 and is normalized by height. Nutritional status should be evaluated within the first 24~48 hours of hospitalization in every patient with cirrhosis. Among the various available screening tools, the Royal Free Hospital-Nutritional Prioritizing Tool proposed in the UK is recommended. Nutritional counseling with a multidisciplinary team is recommended to improve long-term survival in patients with cirrhosis. Multidisciplinary nutrition management should include evaluating nutritional status and providing guidance for achieving nutritional goals. Most guidelines suggest a calorie intake of 25~35 kcal/kg/day, and the recommended protein intake is 1.2~1.5 g/kg/day. One beneficial technique for patients is to divide the total recommended intake across four to five daily meals, including a nighttime snack. The principles of nutritional intervention in cirrhotic patients are not different from those in noncirrhotic patients. For improvement of sarcopenia, a strategic approach including physical activity and exercise, hormone replacement therapy, ammonia-lowering agents, and treatment of underlying liver disease is required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liver fibrosis index and mortality in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease: a Korean cohort study
Yesung Lee, Woncheol Lee
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Liver fibrosis index and mortality in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease: a Korean cohort study
- 11,004 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Significance of Sarcopenia in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing Sorafenib Treatment
- Min-Hyuk Lee, Min-Su Park
- Ann Clin Nutr Metab 2021;13(2):62-67. Published online December 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/ACNM.2021.13.2.62
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between sarcopenia and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Hae Il Jung
Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism.2023; 15(3): 65. CrossRef
- Association between sarcopenia and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- 2,018 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Impact of Preoperative Sarcopenia to Postoperative Prognosis in Patients with Periampullary Malignancy: Retrospective Multicenter Study
- Jee Hyun Park, Youngju Ryu, So Hee Song, Naru Kim, Sang Hyun Shin, Jin Seok Heo, Dong Wook Choi, Woo Kyoung Jeong, Woo Hyun Jung, Yong Chan Shin, Chang-Sup Lim, In Woong Han
- Surg Metab Nutr 2020;11(2):40-45. Published online December 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2020.11.2.40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: This study compared the preoperative nutritional status between sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic patients and examined the effects of sarcopenia on the prognosis after a pancreatoduodenectomy (PD).
Materials and Methods: From 2015 to 2016, 480 patients who underwent PD with periampullary cancer at Samsung Medical Center, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Ilsan Paik Hospital, and Ajou University Hospital were analyzed retrospectively. Sarcopenia was measured from the cross-sectional visceral fat and muscle area on CT imaging using an automatic calculation program. The dysnutritional grade was assessed according to Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score system.
Results: Preoperative serum albumin (3.9 g/dl) and cholesterol levels (161.7 mg/dl) of sarcopenic patients were significantly lower than those of the non-sarcopenia patients (4.0 g/dl, P=0.024; 176.1 mg/dl, P=0.005). The proportion of moderate-to-severe dysnutritional grade in sarcopenic patients was significantly higher than in the non-sarcopenic patients (20.0 vs. 8.1%, P=0.004). A comparison of the changes in albumin between before and after PD showed a decrease in sarcopenic patients (0.06 vs. 0.05, P=0.024). Sarcopenia itself was not a factor affecting the overall survival (OS) negatively, but moderate-to-severe dysnutritional grade was an independent risk factor for OS (HR 2.418, CI 1.424~4.107, P=0.001).
Conclusion: Patients with sarcopenia showed poorer preoperative nutritional status than those without sarcopenia, and the sarcopenia affected the postoperative nutritional status negatively. No direct correlation was observed between sarcopenia and OS, but the dysnutritional grade was an independent risk factor that affects OS. As a result, patients with sarcopenia could be affected indirectly for survival because of their poor nutritional status.
- 659 View
- 0 Download

- Analysis of Muscle Using CT Anthropometry in Major Trauma Patients
- Hang Joo Cho, Yunsup Hwang, Yoon Hyun Lee, Dae Hyun Cho, Dae-Sang Lee, Maru Kim
- Surg Metab Nutr 2020;11(1):12-15. Published online June 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2020.11.1.12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose: The feasibility of nutritional assessment using computed tomography anthropometry has been previously proven. The abdominal muscle at the L3 vertebra is a well-known nutritional biomarker for predicting the prognosis of various diseases, and especially sarcopenia. However, any studies on nutritional assessment of the brain, face, or neck via computed tomography are still scarce. We retrospectively investigated the applicability of the masseter muscle as a nutritional biomarker.
Materials and Methods: Patients who underwent simultaneous brain and abdominopelvic computed tomography at a regional trauma center were retrospectively analyzed. Their masseter muscles at 2 cm below the zygomatic arch and abdominal muscle at L3 were assessed via computed tomography anthropometry. Basic clinical data including trauma information was also reviewed. The data was analyzed in conjunction with the patients’ mortality.
Results: A total of 411 patients were analyzed in the study (316 men and 95 women, mean age: 50.41 years, mean areas of the masseter and abdominal muscles: 10.6 and 137.3 cm2, respectively) and there 146 major trauma patients with an injury severity score higher than 15. The masseter muscle area was decreased in the mortality group of major trauma patients (10.4 vs 7.9 cm2, P=0.001). However, abdominal muscles did not show statistical significance (137.9 vs. 117.7 cm2, P=0.054).
Conclusion: The masseter muscle, when analyzed via computed tomography anthropometry, showed a statistical association with patients’ mortality and it could prove its feasibility as a nutritional biomarker.
- 683 View
- 1 Download

- Relationship of Sarcopenia with the Outcomes of Patients who Underwent Surgery for Bile Duct Cancer
- Hye Jin Kim, Min-Su Park, Bum-Soo Kim, Sang-Mok Lee
- Surg Metab Nutr 2019;10(2):54-58. Published online December 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2019.10.2.54
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose:
This study investigated the impact of Sarcopenia by examining the psoas muscle on the outcomes after bile duct resection for bile duct cancer.
Materials and Methods:
This study retrospectively analyzed 101 patients who underwent surgery for bile duct cancer between January 2006 and December 2015 at Kyung-Hee University Hospital. Skeletal muscle mass was evaluated by performing preoperative computed tomography to define Sarcopenia. Patients were classified into two groups by the median value of the psoas muscle index (PMI).
Results:
The median value of the psoas muscle index in female patients was 463.9 mm2/m2, and the median value of the psoas muscle index in males was 688.7 mm2/m2. In the sarcopenia group, the 1, 3, and 5-year recurrence free survival rates were 74.5%, 52.9%, and 27.5%, respectively. On the other hand, in the non-sarcopenia group the 1, 3, and 5-year recurrence free survival rates were 50%, 34%, and 28%, respectively. In the sarcopenia group, the 1, 3, and 5-year overall survival rates were 84.3%, 54.9%, and 31.4%, respectively. In the non-sarcopenia group, 1, 3, and 5-year overall survival rates were 58%, 40%, and 32%, respectively. However, recurrence-free survival and overall survival were not correlated with sarcopenia (P=0.131, P=0.163).
Conclusion:
Sarcopenia using the psoas muscle index (PMI) has no impact on outcomes of bile duct cancer patients who underwent surgery. (Surg Metab Nutr 2019;10:-58)
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcopenia increases the risk of major organ or vessel invasion in patients with papillary thyroid cancer
Ja Kyung Yoon, Jung Hyun Yoon, Vivian Youngjean Park, Minah Lee, Jin Young Kwak
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Sarcopenia increases the risk of major organ or vessel invasion in patients with papillary thyroid cancer
- 1,119 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Major Surgery in Sarcopenic Patients
- Kyung Won Seo
- Surg Metab Nutr 2019;10(1):5-8. Published online June 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2019.10.1.5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Sarcopenia refers to reduced muscle mass in the elderly population, and this malady is of great interest in clinical course, including postoperative complications and mortality when treating major cancer in the elderly. The definition of sarcopenia varies according to the method of measuring muscle mass, and the skeletal muscle index (SMI) tends to be extensively used in retrospective studies. In many reports, sarcopenia has been reported to be a poor prognostic factor after gastrectomy, colectomy, pancreatectomy and liver transplantation, with regards to complications and the length of the hospital stay. Additionally, patients suffering from sarcopenia have a higher medical burden due to their poor clinical outcome after surgery. To overcome these difficulties, nutritional support and exercise training to improve sarcopenia before surgery is helpful, and so further studies that focus on these treatments need to be conducted.
- 801 View
- 0 Download

- Effect of the Remnant Stomach Volume on the Nutritional and Body Composition in Stage 1 Gastric Cancer Patients
- Koen Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Jung-Bok Lee, Yongbin Shin, Jin Kyoo Jang, Jeong-Hwan Yook, Byung-Sik Kim, In-Seob Lee
- Surg Metab Nutr 2018;9(2):41-50. Published online December 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2018.9.2.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose:
During the first year after surgery, gastric cancer patients experience weight loss and a decline in physical activity. In addition, depravation of the nutritional status and anemia is observed. The decrease in stomach volume is believed to be one of the causes for these changes. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of the remnant stomach volume on nutrition, anemia, and body composition-related parameters in gastric cancer patients after surgery.
Materials and Methods:
A total of 110 patients with stage 1 gastric cancer, who underwent a laparoscopic gastrectomy in 2015 were evaluated in this prospective observational study. Among them, 78 patients received a distal gastrectomy (Billroth 1: 52, Billroth 2: 12, Roux en Y: 14) and 32 underwent a total gastrectomy. The weight, height, and blood test results of the patients were collected during the observation period. The remnant stomach volume, total abdominal muscle area, and subcutaneous/visceral fat area were measured using CT images.
Results:
Patients with a larger remnant stomach volume showed a smaller decrease in the nutritional parameters and better recovery of the hemoglobin level during the first year after surgery. Among the body composition parameters, visceral fat was affected to the greatest extent and subcutaneous/visceral fat were better preserved in the group with a larger remnant stomach volume. In the group with a total gastrectomy, the parameters were worsened significantly compared to the distal gastrectomy group.
Conclusion:
The remnant stomach volume has a protective effect on the body mass index, body weight change, hemoglobin, total protein, cholesterol, and visceral/subcutaneous fat area during the first year after surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimal proximal resection margin distance for gastrectomy in advanced gastric cancer
Amy Kim, Beom Su Kim, Jeong Hwan Yook, Byung Sik Kim
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2020; 26(18): 2232. CrossRef
- Optimal proximal resection margin distance for gastrectomy in advanced gastric cancer
- 1,006 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Sarcopenia in Patients after Pancreatectomy
- In Woong Han
- Surg Metab Nutr 2018;9(2):31-35. Published online December 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.18858/smn.2018.9.2.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Sarcopenia is characterized as a syndrome involving the progressive or generalized loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength with or without increased fat mass. This is one of well-known risk factors for adverse treatment outcomes in patients with various medical and surgical diseases. Sarcopenia itself, independent of the body mass index, is a powerful prognostic factor for cancer cachexia, liver cirrhosis, and even all causes of mortality. In terms of gastrointestinal surgery, sarcopenia is a significant prognostic factor in patients with gastric or colorectal cancers. Sarcopenia is related to postoperative complication, 30-day mortality, overall survival, and disease-free survival after gastrointestinal surgery. For patients with hepatic surgery, sarcopenia is also a significant prognostic factor. Several studies, including meta-analysis, proved sarcopenia to be waiting-list mortality and post-transplantation mortality in liver transplantation patients. Similarly, preoperative sarcopenic obesity was an independent risk factor for death and hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after a hepatectomy. In cases of pancreatic cancer, several studies proposed that sarcopenia was an objective measure of patient frailty that was strongly associated with the long-term outcome independent of tumor-specific factors. In addition, sarcopenia or sarcopenic obesity has been reported to be a strong predictor of major complications after pancreatectomy. As a result, sarcopenia could be used to improve patient selection before a pancreatectomy. The next step to solve the questions to manage sarcopenia and improve the post-pancreatectomy outcomes would be to determine the role of nutrition and physical activity in the prevention or treatment of sarcopenia, and to develop specific medications with an evidence-based treatment of sarcopenia in patients with pancreatectomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Major Surgery in Sarcopenic Patients
Kyung Won Seo
Surgical Metabolism and Nutrition.2019; 10(1): 5. CrossRef
- Major Surgery in Sarcopenic Patients
- 1,198 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Characteristics of Sarcopenia and Cachexia
- Seung-Wan Ryu
- J Clin Nutr 2017;9(1):2-6. Published online June 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/jcn.2017.9.1.2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Sarcopenia, which is defined as a decrease in skeletal muscle mass and strength with aging, is an important risk factor in clinical medicine that is associated with mortality, and poor surgical and nonsurgical outcomes. Sarcopenia is now recognized as a multifactorial geriatric syndrome. Cachexia is defined as a metabolic syndrome with inflammation as the key feature, so cachexia can be an underlying condition of sarcopenia. Recently, cachexia has been defined as a complex metabolic syndrome associated with an underlying illness and characterized by the loss of muscle mass with or without a loss of fat mass. These two conditions overlap but are not the same. In clinical practice, many factors related to sarcopenia (decreased food intake, inactivity, and decreased hormones) are reported frequently in patients with cachexia. On the contrary, systemic inflammation, the core feature of cachexia, can also be present in apparently healthy older sarcopenic patients. This suggests that new therapeutic approaches, alone or in combination, may be appropriate in both conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Implication of Sarcopenia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Seong-Eun Kim
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 71(6): 308. CrossRef
- Clinical Implication of Sarcopenia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- 1,944 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Imaging Techniques for Nutritional Assessment
- Joohyun Shim, Hoon Hur
- J Clin Nutr 2015;7(2):49-53. Published online August 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.15747/jcn.2015.7.2.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Accurate measurement of body composition between lean and adipose tissue mass and distribution of lipid burden may be important in the care of nutritional problems in patients observed in clinical practice and the measurement of outcomes in clinical research. In this review, we discuss the most accurate imaging methods for use as clinical tools in measurement of body composition and distribution. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is a non-invasive technique for assessment of body composition, and the radiation exposure is relatively minimal. However, measurements are influenced by thickness of tissue and lean tissue hydration. Computed tomography (CT) is a gold-standard imaging method for body composition analysis at the tissue-organ level, however the radiation generated by the CT scan is relatively high, thus it should not be considered for a measurement, which can be repeated frequently. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been a useful modality in the assessment of body composition changes in various clinical studies. However, limitations of MRI for assessment of body composition are related to its high cost and technical expertise necessary for analysis. Proper methods for measurement of body composition in specific medical situations like sarcopenia should be evaluated for determination of comparative validity and accuracy, within the context of cost-effectiveness in patient care. In conclusion, an ideal body imaging method would have a significant utility for earlier detection of nutritional risks, while overcoming the limitations of current imaging studies such as DXA, CT, and MRI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ex Vivo, In Vitro and In Vivo Bone Health Properties of Grana Padano Cheese
Cristina Martelli, Luisa Ottobrini, Anita Ferraretto, Paola Bendinelli, Stefano Cattaneo, Fabio Masotti, Milda Stuknytė, Margherita Dall’Asta, Angelo Del Sole, Ivano De Noni, Filippo Rossi
Foods.2025; 14(2): 273. CrossRef
- Ex Vivo, In Vitro and In Vivo Bone Health Properties of Grana Padano Cheese
- 2,058 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KSPEN
KSPEN KSSMN
KSSMN ASSMN
ASSMN JSSMN
JSSMN
 First
First Prev
Prev


